fibre channel (FC)
Fibre Channel(FC) is a high-speed transmission technology developed for high-speed data transfer between workstations, mainframes, supercomputers, storage devices, and displays and standardized by ANSI.
Fibre Channel has neither a channel-type nor a network-type architecture; it combines the advantages of both architectures in a single I/O interface. Such a channel has high flexibility and enables high- performance, high-speed serial transfers using the FCP protocol or other common protocols.
The FC layer model therefore recognizes channel protocols such as Small ComputerSystem Interface( SCSI), Internet SCSI( iSCSI), Single Byte Command Code Set ( SBCCS), High Performance Parallel Interface ( HIPPI), Enterprise System Connection( ESCON) and Fibre Channel Connection( FICON), as well as network protocols such as FDDI, IP protocol and also ATM.
The transmission rates supported by Fibre Channel range from 133 Mbps to 10 Gbps. FC technology can also be adapted to the LAN area using a switch with multipoint addressing capability. Fibre Channel supports both the channel interface and the network interface.
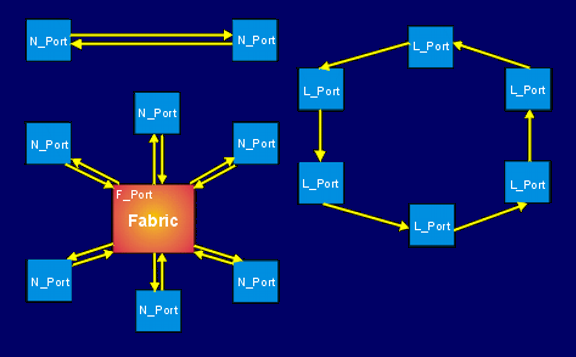
The Fibre Channel topologies
The FC topology is based on a link that is constructed from two unidirectional fiber optic lines. In addition, copper lines can also be used as FC transmission media. Distances of at least 10 km can be bridged with optical fiber, and over 30 m with copper cable. With the introduction of copper-based transmission, "Fiber Channel" was renamed "Fibre Channel".
Fibre Channel is based on port connections and recognizes several FC service classes. The port connections can be a point-to-point connection to a port of a switching fabric, that of a hub or a loop. This means that the Fibre Channel topology available is the pure point-to-point connection, the star-shaped topology with FC switch and the switched ring topology, the Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop( FC-AL).
Fibre Channel has established itself in the high-end of high-speed transfer, it is less suitable for general-purpose LAN use with changing traffic profiles, but is ideal for storage area networks( SAN) and, because of its predictable transfer times, for video transfers. The Fibre Channel was standardized by the ANSI Committee X3T11 in 1994 under the X.3230 standard. This standard defined the 100 MB/s Fibre Channel as a reliable interconnect option with the bandwidth and throughput rates required for disk I/O outside the elite mainframe world. The corresponding transfer rates are 1.0625 Gbps, 2.125 Gbps and 4.25 Gbps.
In 2000, the Fibre Channel Industry Association( FCIA) drew up a new standardization proposal for a 10 Gbit/s fast Fibre Channel: 10GFC, 10 Gigabit Fibre Channel. Another interesting FC concept is Fibre Channel over Ethernet( FCoE).