microwave technics
Microwave technology is a technique with which information or energy is transmitted with microwaves. Microwave technology deals with the generation, amplification, transmission and radiation of microwaves. The microwave range is from 300 MHz to 300 GHz.
The generation and amplification of microwaves
Microwaves are generated using electronic components and resonators that have special properties in this high- frequency range.
In addition to the magnetron and klystron vacuum tubes, which can generate high energy microwaves, there are dielectric resonatoroscillators ( DRO ), traveling wave tubes( TWT), and yttrium-ionron garnet ( YIG) oscillators. In terms of semiconductor devices, transistors, field-effect trans istors( FET), Gunn diodes, high electron mobility transistors ( HEMT), impact ionization avalanche transit time ( IMPATT) diodes, and lateral diffused metal oxide semiconductor ( LDMOS) transistors are used.
The transmission of microwaves
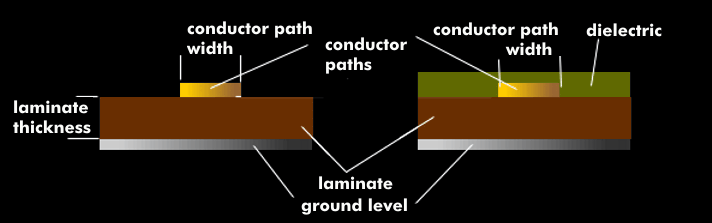
The transmission of microwaves must take into account material behavior and can only take place in a limited frequency range via high-frequency cables. At around 10 GHz, cable-based transmission reaches certain limits, which are reflected in a sharp increase in attenuation. There are microwave connectors and RF connectors with which frequencies up to over 100 GHz can be transmitted, but this is only possible over a limited distance range. Striplines and microstrips have been developed for printed circuit boards over which frequencies of 50 GHz and more can be transmitted.
The behavior of microwaves
High- power microwave signals cannot be transmitted over RF cables anyway, because their attenuation is too high for microwaves. For this reason, higher gigahertz waves are transmitted in waveguides, taking advantage of the reflection of metallic walls. Since certain materials are transparent to microwaves, microwaves can be focused with plastic lenses.
On the other hand, microwaves can be absorbed by certain materials and release their energy to the materials. This ability is determined by the dielectric loss factor of the substance, which depends on the material, microwave frequency and temperature. A best-known example of this is water, which has a very high dissipation factor and causes water to boil in microwave ovens. The prerequisite for this is that the material, in this case water, absorbs the electromagnetic energy of the microwave.
Microwave technology has found its way into a wide variety of applications. For example, as radio technology for baby monitors and garage door openers, in WLANs, Bluetooth and RFID, satellite transmission and microwave directional radio, WiMAX, Local Multipoint Distribution Service( LMDS) and ZigBee, radar systems and mobile communications. In addition, in microwave ovens, plasma systems and materials testing, to name just a few of many examples.