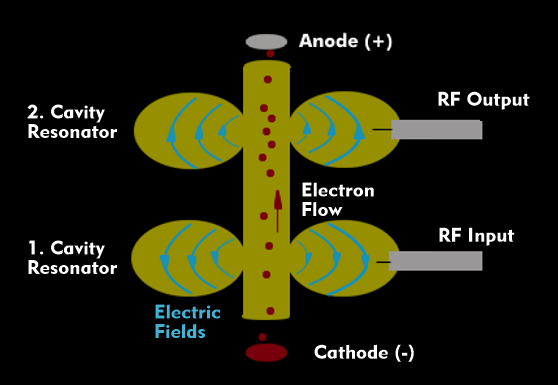
klystron
Klystrons are used to generate and amplifymicrowaves. They are electron tubes with resonators. A klystron consists of an electrode system with cathode, which emits the electrons, and the anode, which receives the electron flow.
The electron flow of the klystron is accelerated by the anode voltage and its speed is modulated by the applied RF voltage. This input voltage is fed through a cavity resonator where it forms a standing wave. The electric field of the standing wave controls the speed of the electron current, which is decelerated and then accelerated again. The control effect is thus amplified.
In a second cavity resonator, the output energy, which is present in the cavity with a high energy, is decoupled. The second cavity resonator must be placed at the point where the change density of the electron beam has a maximum. Only then can a microwave be generated in the second cavity resonator that is much higher in energy than the input RF voltage. The amplified microwave signal can then be coupled out of the second cavity.
Klystrons require at least two cavity resonators, but they can use more than one. The size of the cavity bodies corresponds to the wavelength of the microwaves.
In klystron oscillators, one uses feedback and couples part of the output signal back to the first resonator. Thus a free oscillation is achieved.