router (RO)
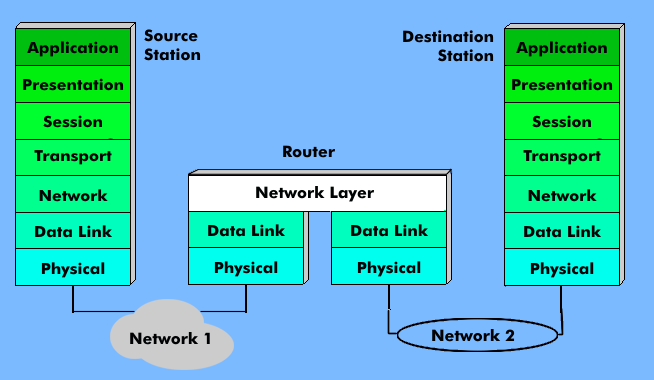
Routers(RO), also called Intermediate System( IS) in OSI terminology, are coupling elements that interconnect two or more subnets at the network layer and realize the functions up to this layer.
In addition to bridging functions, routers can extend the boundaries of a network, their number of stations, and their extent. Furthermore, routers control data traffic by not forwarding data packets containing errors. Furthermore, routers support load separation in subnets by, among other things, filtering broadcasts, they provide advanced addressing functions, and they take care of adjusting the fragmentation and defragmentation of data packets from different network protocols. Furthermore, routers also realize complex routing by implementing different protocols
In contrast to bridges, routers only interpret the data packets that are directly addressed to it; by default, no packet transport takes place. Only if the destination network is known, a packet is forwarded accordingly. Broadcasts are not forwarded, but are processed by the router in the case of routable protocols. Due to the more complex route selection functionality and the prevention of default transport, routers are particularly suitable for LAN interconnection via wide area networks.
Router functionality in the network
The router has the task of establishing an end-to-end connection between two terminals in different subnets at the network layer. It forms the protocol interface between the network and application protocols.
In order to perform the required connection of terminals in different subnets at the network level, routers must realize various functions and basic components. These include a method for identifying stations to the router, such as Address Resolution Protocol( ARP). An algorithm for non-local data packets to select the next router to receive the data packet.
The route determination and its management
Route management includes the creation and maintenance of an information database, the routing table, which contains information about routes and their costs, as well as the number of intermediate stations, hops, and additional transport conditions (e.g., filters). In addition, the forwarding of administrative information to the other routers.
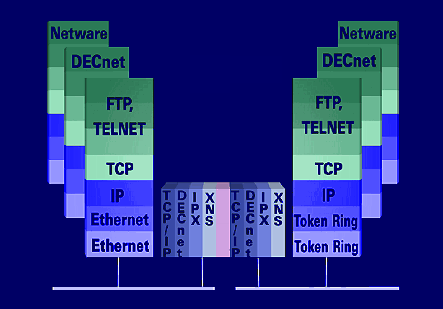
In order to meet the various requirements of different network architectures and transport protocols, there are various types of routers. Thus, a general distinction is made between single protocol routers( SPR), multiprotocol routers( MPR) and hybrid routers. In addition, development has led to a classification of routers according to router performance, not least data throughput and application. Highest performance routers are referred to as terabit routers, or in carrier networks, carrier-grade routers. The following router category with data rates in the gigabit range are the gigabit routers and the enterprise routers. For the backbone area there are core routers, for the transition area the edge router, for the access area the access router and for the small offices the SoHo router.