Gigabit Ethernet (GbE)
The Gigabit Ethernet activities have been processed in the 802.3z and 802.3ab working groups since 1995. Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1GbE) is an Ethernet concept with which a transmission rate of 1 Gbit/s can be transmitted. Gigabit Ethernet is of particular interest for LAN backbones, especially since backward compatibility with the existing 802.3 Ethernet format is ensured, as is the partial preservation of the CSMA/ CD access method.
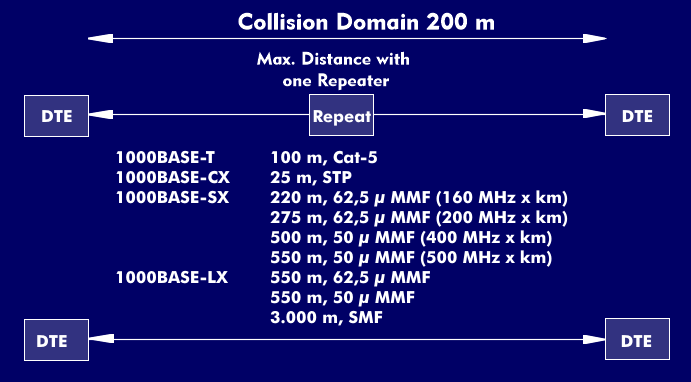
For Gigabit Ethernet, the Ethernet frame according to 802.3 is retained, as is the limitation of the frame length to a minimum of 64 bytes and a maximum of 1,518 bytes. For all transmission media, the collision domain is 200 m. So that this condition could be fulfilled, Gigabit Ethernet has a frame extension, the carrier extension, with which the frame is extended to at least 512 bytes.
Topologies and interfaces of Gigabit Ethernet
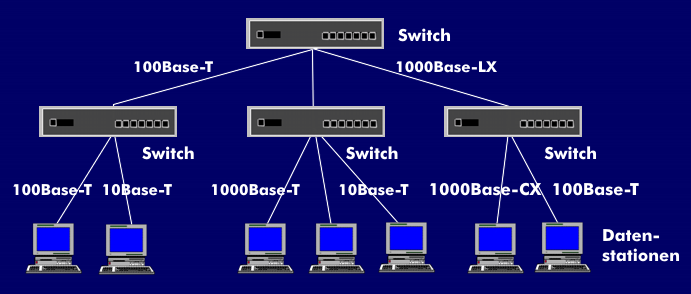
Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) is built in star topology and can work with all transmission media recommended in the ISO/IEC11801cabling standard. In addition, Gigabit Ethernet components can be combined with Fast Ethernet and Ethernet components. The optimum data transmission ratesbetween the 10 Mbit/s, 100 Mbit/s and 1000 Mbit/s components are determined by autonegotiation. In terms of transmission media, the 802.3z working group developed the standards for single- mode fiber, multimode fiber and STP cable, whereas the 802.3ab working group focused on standardizing Gigabit Ethernet on UTP cables in workplace cabling. Category 5 (cat 5) UTP cables with a connection length of up to 100 m can be used in workplace cabling. Category 6 and 7 cables are not provided for in the standard.
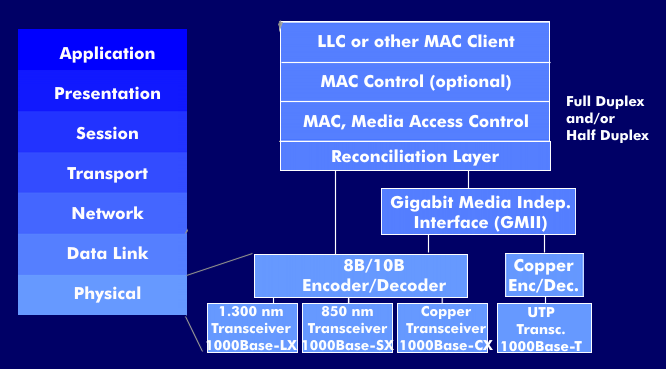
On the one hand, the Gigabit Ethernet architecture defines changes to the existing CSMA/CD process. On the other hand, the GbE layer model includes four different GbE interfaces in addition to the medium access control( MAC), which is unchanged from that of Fast Ethernet except for the higher speed: 1000Base-LX, 1000Base- SX, 1000Base-CX and 1000Base-T. Another Gigabit interface, 1000Base- T1, was developed as part of Single-Pair Ethernet( SPE) for automotive technology and transmits data over a single pair of wires.
Operating modes of Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet offers both full- duplex operation for point-to-point connections and half-duplex. Full-duplex mode is implemented using single-mode fibers or fiber channel with multimode fibers, and distances of 200 m to 2 km can be bridged. In half-duplex mode, fiber channel is used as the basic technology. Gigabit Ethernet uses 4B5B coding or 8B/10B coding as the coding for optical fiber transmission. The first implementations used Fibre Channel with 780 nm wavelength and 8B/10B coding. Current Fibre Channel technologies operate at 1.063 Gbps and can be increased to 1.250 Gbps to achieve the full transmission speed of 1 Gbps.
For backplane Ethernet, the 1000Base-KX interface is a variant for point-to-point connections on STP cables for short distances over one meter.