general purpose interface bus (GPIB)
The General Purpose Interface Bus (GPIB) is an interface bus developed by Hewlett Packard, which has been standardized by various standardization committees under different names. The GPIB bus originated from the HP-IB bus, which was already developed in the 1960s. Hewlett Packard submitted the HPIB bus for standardization in the 1970s to IEEE, which standardized it under IEEE 488 and later under IEC 60488. It was also standardized by ANSI as ANSI MC 1.1 and by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC-625.
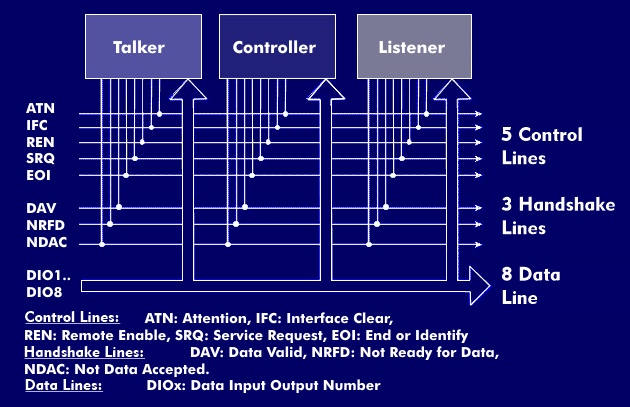
The GPIB bus is a parallel data bus used primarily in measurement equipment and peripherals. The GPIB bus is used for communication between talker, listener and controller. The three components can perform one function or several. For example, a talker can be a listener at the same time, namely when it can send and receive messages. The talker can, for example, be a measuring device that sends measurement data to one or more listeners - which are also measuring devices - or to the controller. The controller monitors and manages the communication and information flow on the GPIB bus by sending commands to all connected devices. It is the central switching point that connects the talkers that want to transmit a message to the desired listener. Before a talker can send its message, it is enabled by control commands from the controller. After the message has been transmitted, the controller can address other talkers or listeners.
There are also GPIB configurations that work without a controller, namely when only one talker is connected to a listener and the talker can only perform a talk function and the listener can only perform a listen function. The controller function can also be executed by a computer and is always needed when different functions can be assigned to the devices.
Connection of peripheral devices
Up to 15 peripheral devices can be connected to a computer via the GPIB bus. It consists of sixteen signal lines and eight ground lines and shields. The 16 signal lines in turn consist of eight data lines, three handshake lines and five control lines for managing the interface. Control commands are assigned to the control lines. For example, the service request (SRQ) or the station enable (REN). The same applies to the handshake lines, which control the validity of the data (DAV) or the rejection of the data (NDAC). The connection between controller, talker and listener is made by a 24- pin GPIB cable with Centronics connector. When connecting multiple devices, the GPIB bus can be looped through the devices or the cable can be equipped with a stackable connector.
As command language GPIB uses the general purpose Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments( SCPI).