distributed coordination function (802.11) (DCF)
Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) is a mechanism in 802.11eWLANs that controls non-deterministic access to the radio network by multiple nodes when access is not controlled by a management device. The DCF mechanism supports voice and multimedia applications in WLANs in terms of performance requirements.
In terms of transmission, WLANs according to IEEE 802.11 are a shared- medium procedure with CSMA/ CA, with which no quality of service( QoS) characteristics can be guaranteed. If stations in a radio network with a collision-free media access method (CSMA/CA) want to access the radio link, they must wait at least for the interframe space ( IFS) specified in the 802.11 standard if the radio network is busy. Only after the Distributed Interframe Space( DIFS) is the radio networkchecked to see if it is occupied or if the station can transmit. In addition to the DIFS time, there are also shorter waiting times, the SIFS (Short) and the PIFS (Point).
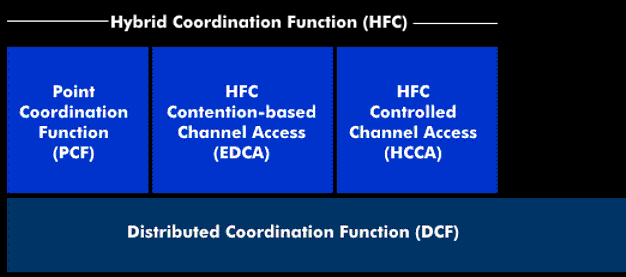
To ensure quality of service such as transmission rate, propagation delay, data loss rate, etc., various coordination functions have been developed, including DCF, Hybrid Coordination Function( HCF) and Point Coordination Function( PCF), which are used in 802.11e.
Since the DCF function does not sufficiently meet the quality of service (QoS) requirements, the Hybrid Coordination Function (HCF) was developed for 802.11e and the DCF function included in it was implemented as a revised EDCF (Enhanced).

.png)