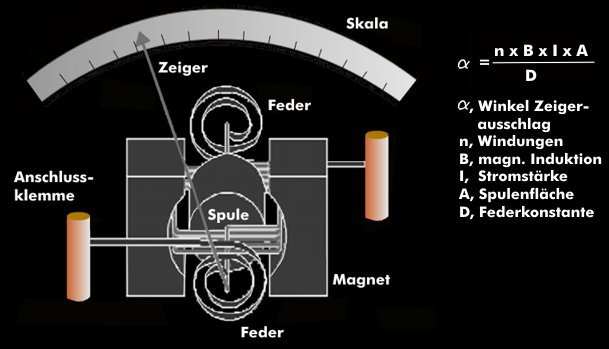
moving coil instrument
The moving-coil movement is based on the electrodynamic principle. It consists of a rotating coil which is located in the magnetic field of a permanent magnet. The current is fed to the coil via two spiral springs wound in opposite directions. The applied measuring current generates a torque which is brought into equilibrium by the spiral springs. The direction of rotation of the coil and the associated pointer depends on the direction of the current.
The angle of the pointer deflection is largely determined by the coil; it is proportional to the number of turns, the coil area, the magnetic induction and the electric current intensity, and inversely proportional to the spring constant. This means that the angle of rotation corresponds to the equilibrium condition between the torque of the coil and the counter-torque of the spiral spring.
The moving coil movement measures the arithmetic mean. If a moving-coil movement is fed with alternating current of technical frequency, the pointer cannot follow the opposing deflection torques and remains in the zero position. For AC measurements, a rectifier is connected upstream in the instrument. The arithmetic mean of the rectified voltage is the rectification value.
The measuring instrument thus first displays the rectified value. In order to be able to read the commonly used rms value of a sinusoidal measurand, the scale is calibrated in rms value by changing the series resistors.
Moving-coil instruments are characterized by a high sensitivity, they have a linearly divided scale display, a relatively high internal resistance and a low external field influence. In addition to the quality, which is determined by the bearing of the moving parts, the internal resistance and the accuracy class are important characteristic values of moving-coil movements. The latter indicate the permissible percentage error in relation to the full scale value. For precision encoders, the classes are 0.1 (0.1 %), 0.2 and 0.5, and for operational encoders, the accuracy classes are 1.0, 1.5, 2.5 and 5.0 (5 %).