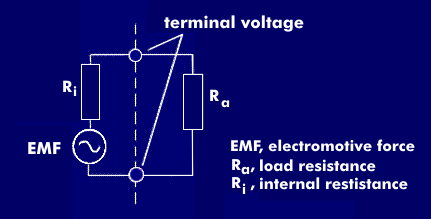
internal resistance (Ri)
The internal resistance represents the internal resistance of voltage or current sources, measuring devices, amplifiers, other quadripoles, batteries or accumulators. For batteries and accumulators, the internal resistance is equal to the sum of all internal resistances.
For batteries, the internal resistance directly affects the terminal voltage, which is the electromotive force( EMF) reduced by the voltage drop across the internal resistance. If the current flow increases, the voltage drop across the internal resistor increases, and the battery voltage and energy efficiency decrease.
Specifically, the internal resistance is composed of the polarization resistance of the electrochemical conversion, the flow resistance of the ions and the ohmic resistances at the electrodes. It increases at low charging currents and when the batteries are frequently partially discharged, which reduces ion permeability.
The internal resistance of the supply source plays a crucial role in constant current sources and constant voltage sources. While the internal resistance approaches zero for constant voltage sources, it approaches infinity for constant current sources.