electromagnetic disturbance
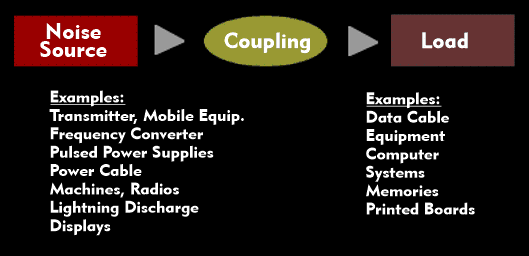
In practice, every electrical device causes (emits) electromagnetic interference( EMI). On the other hand, every device is also a receiver of interference. Conducted interference is transmitted directly via signal lines; field-bound interference as electromagnetic fields.
Capacitive and inductive couplings lead to field-bound interference. Other causes are electrostatic discharges( ESD), square-wave signals, switching operations in networks, induction voltages and lightning discharges( LS).
Electromagnetic interference can be eliminated by various measures. These include grounding, galvanic coupling, line filters, shielding, use of coaxial cables and TP cables, parallel routing of conductors, conductors of the same length and constant resistance, avoidance of unnecessary switching operations and attention to low emissions.
In order to guarantee the goal of electromagnetic compatibility( EMC) and to largely eliminate electromagnetic interference, the EMC Directive 2004/108/ EC, which will then replace the old Directive 89/336/EEC, must be complied with from July 2009. In the Federal Republic of Germany, the EMC Directive has been implemented in the Electromagnetic Compatibility Act(EMVG). It applies to all devices, systems and equipment and networks that contain electrical or electronic components.