Mirasol-Display
Mirasol technology is a reflective display technology developed by Qualcomm for e-book readers and smartphones. Reflective technologies, such as those used in LCD displays, electronic paper displays( EPD) and memory-in-pixel( MIP) displays, among others, operate in a power-saving manner and in bright ambient light. They do not emit light. Mirasol displays are used in e-book readers and, unlike EPD displays, can display multiple colors. They require power only during image changes; in a static state, they do not require power.
Mirasol technology differs fundamentally from e-ink technology, in which small white and black pigments are rotated by electric fields. Mirasol technology is based on microsystems technology( MST), whereby tiny metal membranes move on a micrometer scale and the interference of incident light provides the colored display.
The micro-metal membranes can be changed so quickly that these displays can also be used to show videos and animations.
Color representation via interference
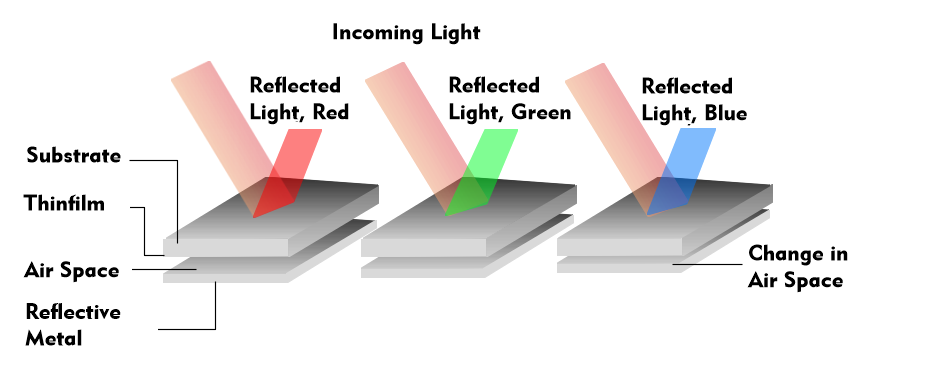
Mirasol color displays are based on a reflective technique that creates interference in an interferometric modulator (IMOD). This is a microsystem technology component that uses incident light and does not require a backlight, saving the power needed for the backlight.
In the Mirasol display, each individual color pixel consists of two conductive plates. One is deposited as a thin film on a glass substrate, and the second is a reflective membrane located below the thin film electrode. Between the two plates is an air gap that determines the color produced by the interference. The wavelength range of the interference is between 380 nm and 780 nm, depending on the plate spacing. There are color pixels for red, green and blue( RGB), which differ in the air gap.
These IMOD elements, designed in microsystem technology and only a few micrometers in size, operate bistably and have two stable states. When no voltage is applied to the two conducting plates, the plates are separated, i.e., the air gap is present and light is reflected from the lower membrane. When a voltage is applied, the two microplates are pulled together by electrostatic fields and the incident light is absorbed, no light falls back. This state corresponds to black. As with other displays, any other color of the RGB color model can be produced by mixing red, green, and blue colors by turning the color pixels on and off. For example, if the color cyan is to be produced, then the IMOD elements for green and blue are activated; for white, all three IMOD elements are switched on.