electronic paper display (EPD)
Electronic Paper Display(EPD), also known as e-paper, attempts to replicate the properties of paper as far as possible: thin, light, flexible, good contrast and no light reflections. Such displays are ideal for e-book readers because you can use them even in sunlight and high ambient brightness. In addition, the e-paper technology is extremely power efficient.
Technically, the Electronic Paper Display is an extremely thin, flexible, electrophoresis-based bistable display with a thickness of less than 300 µm that uses reflective technology. This means that, as with paper, the typeface and images are only visible when ambient light falls on the display. In the electrophoretic display, the individual pixels are switched to one of two stable states and remain in this state until they are changed again. This has the advantage that the e-paper has extremely low power consumption because it only requires power when the page content changes. This advantage over other display technologies is reflected in the extremely long battery life. Moving image display is not possible with these displays.
The structure of the Electronic Paper Display
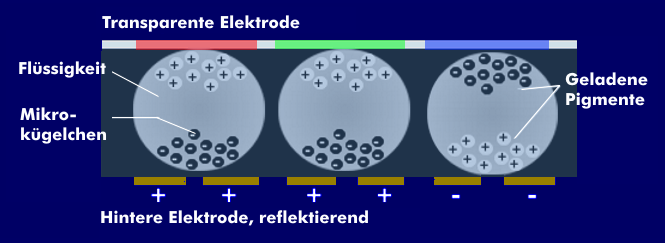
In terms of structure, E-Paper or E-Ink, developed by the E-Ink company, consists of two electrodes between which there are microcapsules filled with a clear liquid. The upper electrode is transparent. The lower electrode, an active matrix, generates the electric fields for the individual microcapsules. This electrode is opaque and reflects light. Electrically charged black and white beads move in the microcapsules, which are controlled by electric fields. Since the beads have different charges, they react differently when voltage is applied. For example, the black beads have a negative charge and, when a negative voltage is applied to the lower electrode, are repelled by it, causing them to migrate to the upper electrode and thus creating the impression of a black pixel.
Another e-paper that works on a similar principle to e-ink was developed at Xerox PARC and is called Gyricon.
Characteristics of EPD displays
E-Paper can also display the individual pixels in up to 16 gray levels. It has a resolution of well over 100 pixels per inch( ppi) and a contrast ratio of 10:1. The screen sizes of EPD displays used in e-book readers range from 6" to the size of DIN A4. EPD displays are equipped with rechargeable batteries and larger memories that can easily store a hundred or more e-books. Since the switching speed of the individual pigments is relatively sluggish, such technologies are not suitable for video or moving image displays.
The process developed by E-Ink was first introduced in 2016 under the name Advanced Color e-Paper( ACeP) for color displays. Others have modified the e-paper process. For example, there is an EPD display in which the powder pigments do not float in liquid, but instead float as a fine powder in small air chambers. In addition, several companies have developed color EPDs that use colored beads or color filters.
Application scenarios for EPD displays
As e-paper technology evolves into lightweight, low-cost plastic substrates, EPD technology can also be used for price tags, shelf labels and information signs. Changes to the signs could be implemented by radio technology. Application scenarios are also realistic for luggage tags. So are timetables for buses, ships and trains.