gunn diode
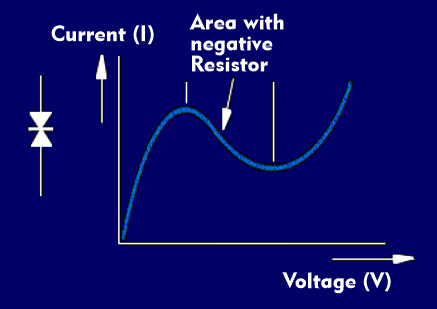
In semiconductors, there are certain effects that are used in circuitry. In the case of the Gunn diode, it is the Gunn effect, which takes its name from its discoverer J. B. Gunn. In 1963, Gunn discovered that semiconductors with identical but different doping levels have a negative differential resistance.
The Gunn effect is based on the fact that electrons in n-doped semiconductors, which have differently doped semiconductor regions, can jump from one energy band to a higher energy band when energy is applied. In the higher energy bands, the electrons are less mobile, which translates into greater field strength at lower current. This means that the Gunn effect requires a higher current at lower voltage and a lower current at higher voltage. The resistance is therefore differentially negative in this range.
This Gunn effect is used with the Gunn diode for high frequency oscillators. Gunn diodes can be used in the frequency range between 1 GHz up to 100 GHz for oscillation generation.
In terms of structure, Gunn diodes consist of an n-doped semiconductor material, with three different strength n-regions: the upper, middle and lower regions. The upper region is relatively heavily n-doped, and the middle region is the active region. It has a width of about 10 µm, but it changes and is the frequency-determining region. This zone is less heavily doped. The Gunn diode has no pn junction. The power that can be achieved with Gunn oscillators can be from 100 mW to 300 mW.