dissipator
Heat sinks, heatsinks or dissipators, are mechanical components that dissipate the power loss of electronic components. Heat dissipation and cooling are necessary so that the components have optimal thermal working conditions and are not limited in their functionality by excessively high temperatures, thereby reducing reliability.
For this heat diss ipation, specially shaped bodies are placed directly on the electronic component - the transistor, thyristor, light-emitting diode or chip. The thermal contact is often increased by thermal conductive pastes so that the heat sinks achieve the greatest possible heat dissipation.
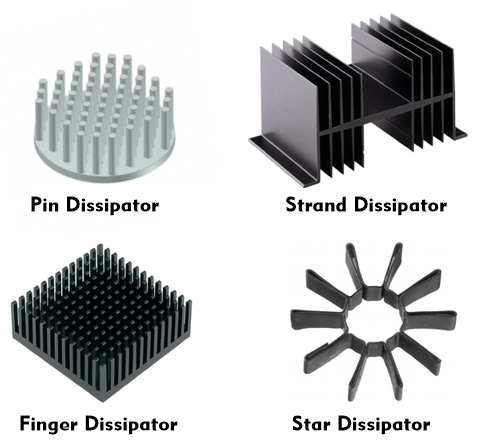
In addition, the surface area of the heat sinks is made as large as possible by abstract shapes. Among the various designs, there are pin heatsinks, finger heatsinks, string heatsinks, cooling star and the tube heatsink, also known as heat pipe.
The heatsinks themselves are made of particularly thermally conductive materials such as copper, aluminum, brass, steel or alloys, materials that are characterized by high, sometimes much better thermal conductivity than aluminum and copper. Annealed Pyrolytic Graphite (APG) is such a heat-conducting material, which has up to five times the thermal conductivity of copper. If heat dissipation by means of heat sinks is not sufficient, additional fans can be used to ensure better air circulation.