ATM address
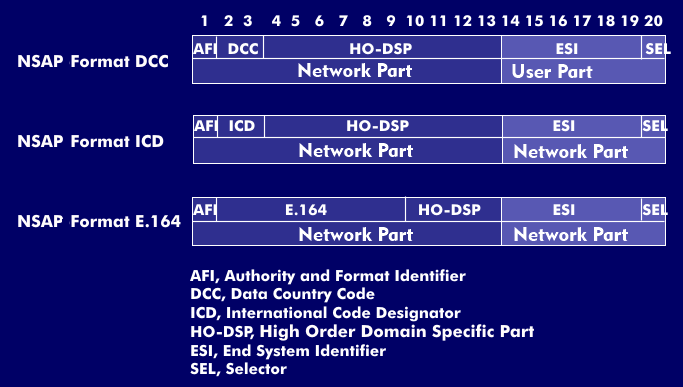
The ATM address structure is a hierarchical address system for the Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). The ATM address structure is specified in the User Network Interface( UNI) and distinguishes between three different formats with a length of 20 bytes. All three formats - the NSAP format with Data Country Code( DCC), with International Code Designator( ICD) and according to E.164 - refer to the Network Service Access Point (NSAP) and consist of the network part and the end user part.
The network part in turn comprises 13 bytes and, in all three formats, consists of a one- byte data field for the Authority and Format Identifier( AFI) and either the Data Country Code (DCC) for public networks, which comprises two bytes, and the High Order Domain Specific Part ( HO-DSP), which consists of ten bytes. In the second address format, the ICD data field takes the place of the DCC data field, with the International Code Designator (ICD) for private networks, and in the third address format, the E.164 data field takes the place of the ICD data field, although it comprises 8 bytes. In this version, the HO-DSP data field is reduced to four bytes.
The end user part is the same for all address formats and consists of the 6 byte resp. 48 bit long End System Identifier( ESI) and the Selector( SEL) data field, which comprises one byte. With this constellation the country code, the area code and the end system can be identified.