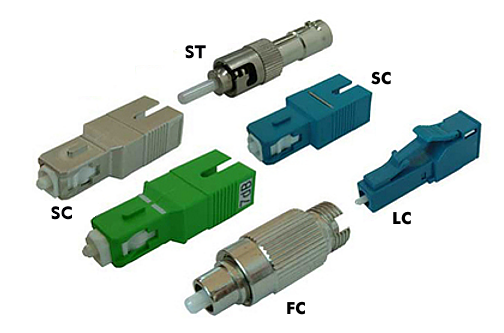
optical attenuator fiber (OAF)
Optical attenuators are used in optical transmission systems to attenuate the optical signal level. They are available with fixed attenuation values, with stepwise adjustable attenuation and as variable optical attenuators, Variable Optical Attenuator (VOA).
Among the variable attenuators, there are those that are manually adjustable, while others are programmable. Typical attenuation values for fixed attenuators are between 2 dB and 30 dB, for variable attenuators the attenuation range is up to 60 dB. Optical attenuators are available for single- mode, multimode, and gradient fibers with face coupling and helical coupling, and for all FOC connectors.
Optical attenuators operate on several technical principles, one of which is based on air- gap control between two optical fibers, while other techniques use absorption and reflection of light waves. Since distortion can occur upstream of the attenuator in some attenuation techniques, such attenuators should be installed at the end of the transmission link.
In addition to attenuation and its accuracy, insertion loss and return loss are important characteristics of optical attenuators. Furthermore, it is decisive for which optical waveguides and which wavelengths the optical attenuators can be used. As a rule, they are suitable for wavelengths from 850 nm, from 1,260 nm to 1,310 nm and 1,460 nm to 1,550 nm.