multi level coding (MLC)
In the 1970s, modulation techniques were combined with channel coding and founded as coded modulation. These techniques were constantly optimized and led to digital, bandwidth-efficient transmission methods. Many coded modulation techniques use pulse amplitude modulation( PAM), phase mod ulation( PM), and quadrature amplitude mod ulation( QAM).
All methods of coded modulation are multi- level coding ( MLC), where the pulse amplitude consists of several levels and each level represents a bit or a combination of bits. In principle, the number of levels can be any number.
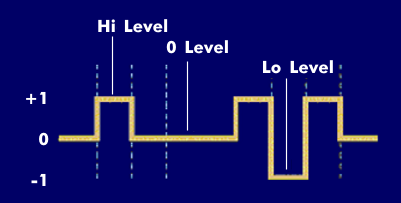
Since each level is assigned a bit combination, not only one bit is transmitted with each modulation step, but two bits, three bits or more. Thus a three-level coding, as used in the ternary method, has the three levels +1, 0 and -1. The logical value 1 can be assigned to the +1 level, and the logical zero to the -1 level. The 0 level can be used for error correction, for example.
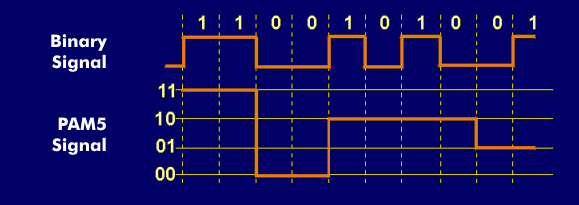
In five-level pulse amplitude modulation, PAM5, there are amplitude levels +2, +1, 0, -1, and -2. These five levels can be assigned the four bit combinations 00, 01, 10, and 11 as dibits, and the fifth level, the 0 level, can again be used for error correction.
Multilevel coding schemes can also use 8, 12, 16, 24, 32, or 64 levels and have the advantage that the number of levels also increases the number of binary codes, but at the same time reduces the symbol rates for transmission. Examples of this are 8PAM and 12PAM, but also 16QAM or 64QAM, whereby the phase angle is also changed in these coded modulations.