axial displacement
The term axial displacement is used in optical transmission technology. Axial displacement refers to the eccentricity of the core glass area of two coupled optical waveguides(FOC).
Axis displacement can occur in splicesand LwL connectors due to the offset of both optical fibers in the axial direction. When the core glass surfaces do not match, not all of the light signal from one optical fiber is coupled into the other, and the coupled light signal is attenuated. The adverse effects are similar to overfilled launch( OFL) and underfilled launch (UFL).
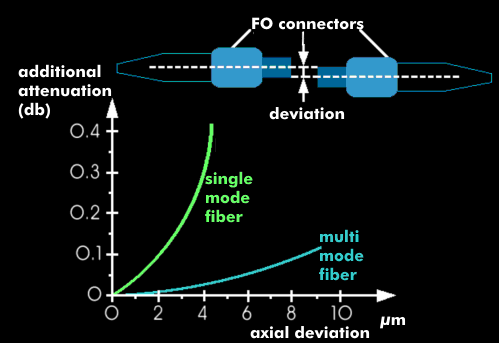
The damping depends on the diameter of the core glass and the offset. An axis offset between two coupled optical fibers produces attenuation values of several decibels ( dB), depending on the size of the lateral offset, i.e., the offset in the axial direction, and on the optical fiber.
The smaller the core glass diameter, the more critical it is to establish a match between the core glass surfaces. For monomode fibers, for example, an axial offset of only 4 µm causes an attenuation of approx. 0.4 dB.