virtualization technology (VT)
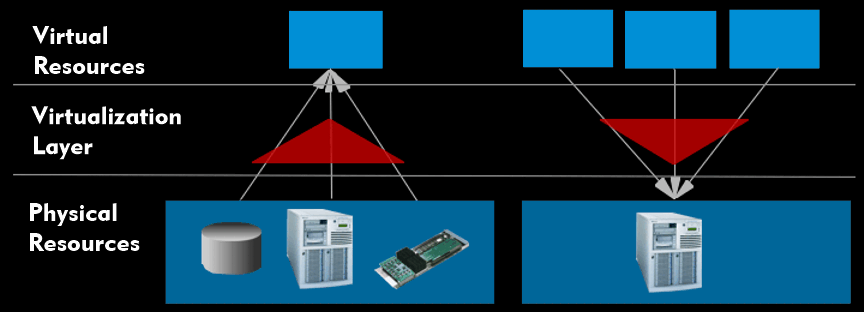
Virtualization enables the abstraction ofhardware, software and networks. In an overarching sense, virtualization refers to software or hardware techniques that implement a layer of abstraction between the user or applications or interfaces on the one hand and physical resources such as hardware components of a computer on the other.
This abstraction layer is used to logically combine multiple resources so that they present themselves to the user as a single component, such as to make multiple computers appear as one computer, or conversely to split a resource so that the user has multiple logical components available. As in, for example, a hard disk with multiple partitions.
The virtualization layer hides the implementation details of the system in use and decouples the overlying components from the underlying hardware. In practice, virtualization is used to make more flexible and efficient use of hardware and its components, e.g. server virtualization allows multiple operating systems to share a single computer as virtual machines( VM) and use it simultaneously.
Virtualization can be implemented at many different levels:
- Hardware partitioning divides a computer into several virtual machines at the hardware level.
- Grids combine many computers into a virtual supercomputer.
- Storage systems can logically combine or divide storage areas.
- Central processing units (Intel VT, AMD-V) can allocate their own runtime and storage areas to virtual machines.
- Operating systems and special virtualization layers such as Virtual Machine Monitor( VMM) or Hypervisor provide isolated runtime environments.
- Application virtualization allows applications to run in a virtual environment without being installed locally.
- Applications provide virtual instances of themselves, e.g. virtual hosts for web servers.
- In virtual runtime environments, applications are decoupled from the underlying operating system in a virtual machine and can thus run in different environments. Example: Java Virtual Machine( JVM).
- Desktop virtualization abstracts from the normally required local computer system by running the desktop virtually on another computer as in terminal services, server-based computing or by transparently transferring a centrally stored desktop (only) to the local system at runtime.
Last but not least, virtualization is an interesting tool for reducing energy costs in connection with the demands for green IT. By optimizing the utilization of their servers through virtualization, companies can significantly reduce the size of their server farms and thus save energy.