tunneling
Tunneling is the name of the process in which two different protocols are encapsulated with each other on the same layer. The data of one protocol is packed into the data packets of the second protocol.
Tunneling is used when transitioning from one protocol to another, such as in" IP over ATM"( IPoA). It is used to transport data over an insecure public network, such as the Internet, between a central VPN gateway and a remote VPN client. A virtual connection is established between the endpoints. A tunnel is established by giving each data packet an additional IP header, plus one or more special header fields. The starting point of the tunnel is where the IP header is added, the end point where it is removed again. Authentication and encryption take place within the tunnel.
The standard method used for transporting multiprotocol datagrams is the Point-to-Point Protocol( PPP) or the MultilinkPPP Protocol( ML-PPP).
Tunneling on layers 2 and 3
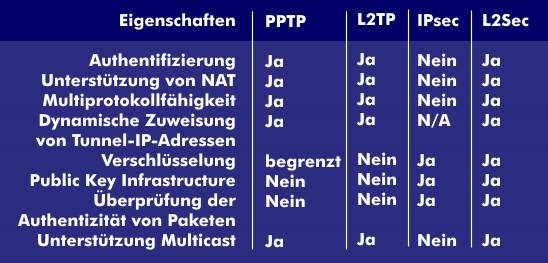
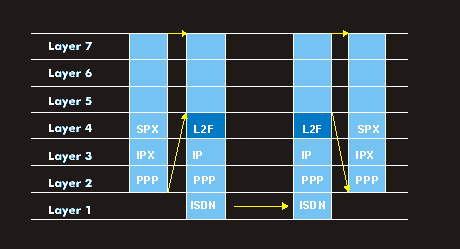
Tunneling can be performed at Layer 2 and Layer 3. A Layer 2 tunnel is equivalent to a "virtual cable" that can be built across the IP platform. It is multi-protocol capable and supports Internetwork Packet Exchange Protocol( IPX), System Network Architecture( SNA), DECnet or NetBIOS in addition to the IP protocol. Level 2 protocols for tunneling include the Point to Point Tunneling Protocol( PPTP) supported by Microsoft, Generic Routing Encapsulation( GRE), Layer 2 Forwarding( L2F) from Cisco, the Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol ( L2TP), which combines the advantages of both methods and is standardized, and Layer 2 Security ( L2Sec).
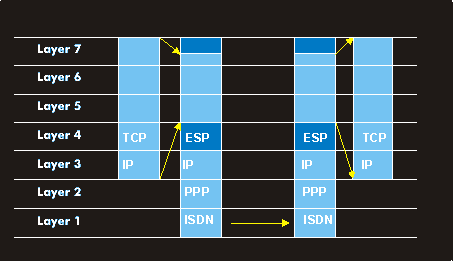
In contrast to Layer 2 tunneling, tunneling on Layer 3 of the OSI reference model is not multi-protocol capable. It always refers to a specific network protocol, such as the IP protocol. With IPsec, a tunnel can be established for the IP protocol with corresponding security. RFCs 2401 to 2409 describe how a corresponding virtual private network (VPN) can be set up . There is also the Generic Routing Encapsulation protocol (GRE) according to RFC 1701, which is very similar to IPsec but incompatible with it. Other protocols include Mobile-IP, which is the subject of an IETF working group, Virtual Tunneling Protocol(VTP), which uses Generic Routing Encapsulation for encapsulation, and proprietary tunneling protocols.