light triggered thyristor (SCR) (LTT)
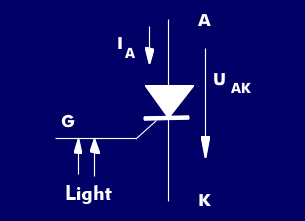
A Light Triggered Thyristor (LTT) is a light-controlled switch, a Light-Activated Switch (LAS). LTT thyristors are triggered by light signals and are mainly used in high- voltage technology and high-voltage direct current ( HVDC) transmission. Light triggering greatly simplifies thyristor control. The LTT thyristor is switched off by current reversal.
The difference between an electrically triggered thyristor, Electrically Triggered Thyristor (ETT), and a light triggered thyristor is that the gate of the light triggered thyristor is connected to an optical fiber and is triggered by a short laser pulse. The gate is protected by a breakover diode( BoD). The gate structure of the LTT thyristor responds to specific wavelengths, releasing electrons and firing the thyristor. The control of the thyristor is floating.
The excess charge carrier is increased by a current rise between the gate and cathode, causing the thyristor to turn on. The light power for gate control is less than 50 mW, the pulse duration of the light pulse is a few microseconds, and the light wavelengths are in the visible light range or in the infrared range at about 1,000 nm.
LTT thyristors can switch high voltages of more than 10 kV and currents of several kilo-amperes. They can withstand current surges of well over 100 kA.

-Foto-Infineon.png)