transponder
Transponders, a made-up word from transmitter and responder, are used in high- frequency transmission systems with satellites, in terrestrial systems, in RFID and in optical networks. They are used for frequency or wavelength conversion from one frequency or one wavelength to another.
Transponders in satellite transmission
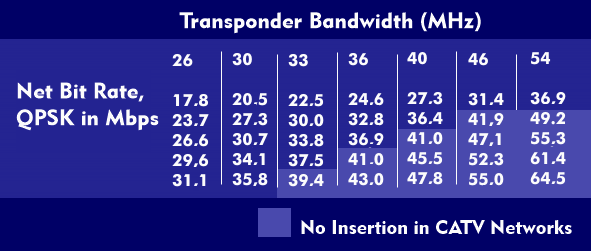
Insatellite transmission, satellite transponders handle all the message processing of the signals. They receive the uplinksignal from the earth (14 GHz), transform it to a lower frequency of 11 GHz to 12 GHz, amplify it and transmit it back to earth as a downlink signal. The bandwidths at which transponders operate depend on the satellite transmission and range up to 72 MHz. Common bandwidth values are 26 MHz, 30 MHz, 33 MHz and 36 MHz.
Satellite transponders are divided into transparent and regenerative transponders. In the transparent transponders, the frequency is converted and the signal is amplified. The regenerative transponders have all the functions of the transparent transponders, in addition they work with a regenerator with which the signal is also regenerated, they have on- board processing (OBP) for demodulation, signal conditioning and remodulation. With the regenerative approach, noise can be reduced, the transmission quality of the channel can be improved, and multiple single channel per carrier( SCPC) or TDMA channels can be combined into one TDM downlink channel.
Satellite transponder gain ranges from 100 dB to 120 dB, and transmit power can be as high as 100 W. Communications satellites typically have twenty or more transponders. In order for the transponders to make the best use of the available frequency bands and transmit as many television channels as possible in them, the carrier frequencies are radiated in different polarizations: Horizontal and vertical as well as left and right circular.
Transponders in RFID technology
In RFID, the contactless data carrier is the transponder. It consists of a coupling element, an antenna coil or a dipole antenna depending on the RFID frequencies, and a microprocessor. The transponder, which is located in the RFID tag, has no power supply of its own in passive RFID systems, but obtains its supply voltage from the electromagnetic fields emitted by the RFID readers. It is passive and is only activated within a certain operating distance of a reader.