transition minimized differential signalling (Monitor) (TMDS)
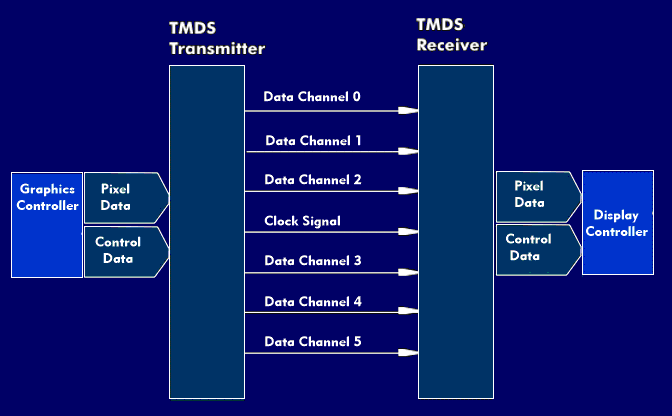
Transition Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS) is a transmission protocol used to transfer the digitalsignals of the primary colorsred (R), green (G) and blue (B) and a clock signal between personalcomputers(PCs) and displays.
The TMDS protocol is characterized by the fact that it minimizes the voltage transitions of the differential signaling. To do this, TMDS uses an exclusive- OR function, XOR, or an XNOR gate. By minimizing transient voltage transitions, voltage spikes on the cable that affect electromagnetic compatibility( EMC) are avoided. Prior to transmission, 8B/10B coding is used to convert the 8-bit data stream to a 10-bit data stream.
TMDS is used in various digital interfaces such as the Digital Flat Panel( DFP), Plug and Display(PnD), High Definition Multimedia Interface( HDMI) and the Digital Visual Interface( DVI).
For the DFP interface, the clock frequency is 85 MHz, for PnD it is 160 MHz, and for the DVI and High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI), the clock rate is 340 MHz, although this is related to the doubling of the number of channels to 2 x 3. The two links, each with three channels, allow screen resolutions to be displayed in Quadruple XGA( QXGA).
This method has been standardized by the Video Electronics Standards Association( VESA) in the panel link and is used on the DFP interface, the DVI interface and the PnD interface.