three-phase current
Three-phase current is three-phase alternating current. The three phases of three-phase current are 120 degrees out of phase with each other. The difference to single-phase alternating current lies in the level of the alternating voltage and the transmittable current power, since each individual phase can carry as much current in terms of power as the one phase of single-phase alternating current.
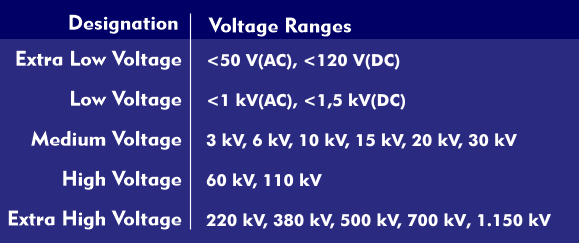
Since AC electrical power is almost always generated in three phases, the power is also transmitted in three phases to the end user, whether to industrial plants, office buildings, or to residential buildings. Power grids for high voltage, medium voltage and low voltage are available for three-phase power transmission.
In three-phase low-voltage networks, each of the three out-of-phase voltages in the outer conductor with respect to the neutral conductor has an effective voltage of 230 V. The rms value between any two phases is 400 V. Consumers can use the 230 V or the 400 V, depending on the connection.
The supply of terminal equipment with high power consumption is much more efficient with three-phase alternating current than with single-phase alternating current. As far as end devices in residential buildings are concerned, instantaneous water heaters, electric ovens and heat storage units, among others, are connected directly to three-phase current. One advantage of three-phase current is also simpler wiring, since no neutral conductor is required for three-phase connections. On the other hand, for normal household appliances, you can only connect one phase with a neutral conductor and have a mains voltage of 230 V.