thermoelectric (TE)
Thermoelectrics is a technical discipline that deals with the conversion of heat into electrical energy. One area of thermoelectrics is the use of waste heat from electronic components, technical devices, engines, power plants, industrial plants, motor vehicles or from environmental heat, as in energy harvesting.
Thermoelectrics, like other alternative energies, can contribute to the generation of energy from waste heat and ambient temperatures. It is based on two effects discovered in the 19th century: the Seebeck effect and the Peltier effect. In both effects, which occur together but are used separately in thermocouples and thermogenerators, thermoelectric voltages are generated from temperature differences or, conversely, heat or cold from voltage differences.
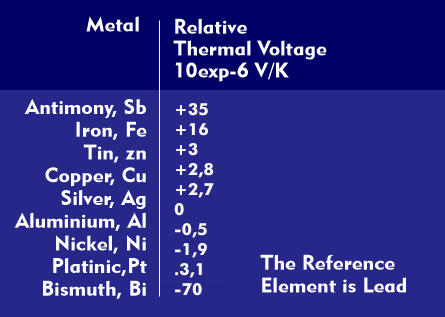
The effects mentioned are based on different thermoelectric voltages that metals or metal alloys exhibit. Since the efficiency of thermoelectrically generated voltages in metals is extremely low, only a few microvolts per degree Celsius, this technology has only been used to a limited extent in components.
It was not until newer compound semiconductors replaced the earlier metal alloys that the efficiency was substantially increased. Bismuth telluride and lead telluride are used as compound materials. Further increases in efficiency have been achieved through improved nanoscale structuring. Despite these improvements, the efficiency currently achievable is only a few percent.