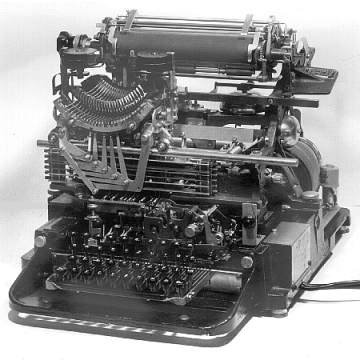
teletype (TTY)
A teletypewriter (TTY) is comparable to a typewriter that generates pulses for each character, which are transmitted to a receiving station, converted back into characters by the latter and printed out. For this purpose, the keys of the teletypewriter have electrical contacts whose signals are transmitted to the remote receiving station.
The characters produced by the teleprinter are encoded with the character set of the IA-2 alphabet, known as the 5-bit telegraph code. Data is transmitted between the teletype and receiving station at a data rate of 50 baud, which is equivalent to 400 characters/min. Teletype (TTY) is also used for asynchronous transmission to dumb terminals.
To make better use of the capacity of the teletype line, messages are usually not sent directly, but punched into a punched tape, which is then read by the teletype and transmitted over the teletype line. Because of their reliability, teletypes are still in use today, although at 50 bit/s they are the slowest of all data facilities.
Telex systems had their own national and international numbering plans, which had nothing to do with the numbering plans of telephone networks. Telex country codes were 2 and 3 digits, with the first digit indicating the world region or service. After that, North America had 2 as the leading digit, South America had 3, and Europe had 4 and 5.