short wave division multiplexing (SWDM)
Short Wave Division Multiplexing (SWDM) is a wavelength division multiplexing technique used in Ethernet that operates with short wavelengths of light. Generally, Ethernet operates in the optical window at 850 nm over multimode fibers.
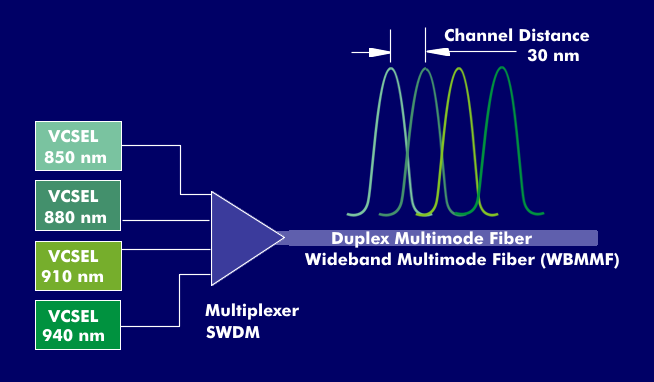
SWDM technology has been ratified by the SWDM Alliance. SWDM operates at four wavelengths of 850 nm, 880 nm, 910 nm and 940 nm, each generated by a VCSEL laser. Since the multimode fibers used in Ethernet are only suitable for the optical window at 850 nm, they are unsuitable for other wavelengths. For this, the attenuation values and the data rates are limited and not specified. SWDM technology therefore uses a broadband-optimized multimode fiber, Wideband Multimode Fiber(WBMMF), which complies with OM class OM5.
Due to the relatively wide spacing between the individual wavelengths, unwanted interference that can be caused by the pulse scattering of the VCSEL lasers is avoided. If 10 Gbit/s are transmitted over each of the four wavelengths, the total data rate over a multimode fiber will be 40 Gbit/s. The wavelengths multiplexed onto the transmit line are separated again on the receive side using an optical splitter. The SWDM technique can be scaled for other data rates. For example, if 25 Gbit/s are transmitted over each wavelength, then 100 Gbit/s are transmitted over the four wavelengths.