sea cable
Submarine cables are used to describe communication cables and also submarine power cables for high- voltage direct current ( HVDC) transmission. In the age of satellite communications, the term submarine cable or undersea cable sounds like a relic from times past.
Even though the first submarine cables were laid in the 19th century, they have lost none of their importance today - on the contrary. Without the fast communication links via submarine cables, many communication services could not be realized, on the one hand because of the low delay times compared to satellite communication, and on the other hand because of the enormous bandwidths that cannot be realized with either satellite communication or directional radio.
Submarine cables for communications and message transmissionare continental and intercontinental cable links laid on and in the seabed. For this purpose, the seabed is flushed up with high pressure and the submarine cable is laid in the resulting trench. The washed-up sand then solidifies again.
Submarine cables have a much shorter transit time than satellite links and have extraordinary bandwidths thanks to state-of-the-art fiber optic technologies. They form the essential communication arteries of global networking.
The historical development of submarine cables
Historically, submarine cables in the mid-20th century consisted of coaxial cables for 8 or 24 voice channels. Depending on the cable attenuation, cable amplifiers had to be installed every 20 km or 30 km to compensate for the frequency response drop and cable attenuation. It was not until the advent of fiber optic technology that it was possible to install much broaderband submarine cables for several million voice channels. Here, optical amplifiers( OA) such as erbium doped fiber amplifiers( EDFA) or optical repeaters( OR), which are supplied via additional copper cables or via the metallic protective sheaths, took the place of cable amplifiers. Since all optical amplifiers are in series, the characteristics of the optical amplifiers accumulate, resulting in higher noise or elevation of certain wavelength ranges over long, intercontinental distances. To increase the usable bandwidth, the optical fibers are operated with wavelength division multiplexing(WDM). A further increase in bandwidth up to several terabits per second (Tbit/s) is achieved by low attenuation single mode fibers and dispersion compensated optical fibers.
These data rates result from the transmission speed of 10 Gbit/s per wavelength. For wavelength division multiplexing with 16 wavelengths, this results in a total data rate of 160 Gbit/s/fiber. If DWDM with 40 wavelengths is used instead of WDM, the transmission rate per optical fiber would be 6.4 Tbit/s.
In the meantime, submarine cables with a transmission capacity of over 50 Tbit/s are already being implemented.
The topology of submarine cables
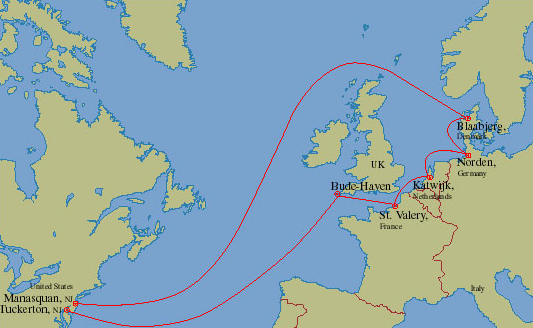
Topologically, submarine cables generally form a point-to-point connection. However, there are also concepts in ring topology, such as the TAT-14, the transatlantic telephone cable No. 14. This has the advantage that, in the event of failure of one link, communication can be maintained via the ring.
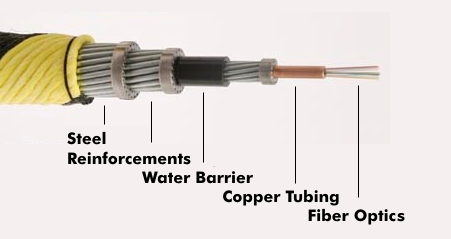
The submarine cable itself is a steel cable armored with a polyethylene( PE) jacket, water barriers, protective sheaths, and a copper or aluminum tube that may contain a hundred or more optical fibers. Power is supplied to the optical amplifiers through the conductive copper pipe and seawater.
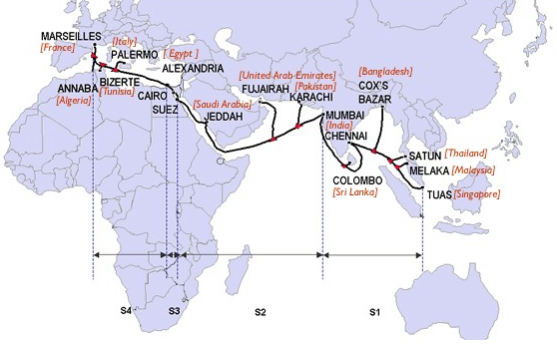
Submarine cables are used where there is a high demand for communications, such as between Europe and North America, in the Mediterranean area through the Middle East to Southeast Asia, between Japan and Taiwan, and between East Africa and Europe.