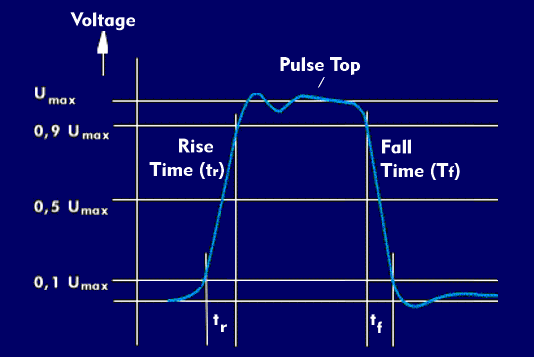
rise time (tr)
The rise time (tr) plays an important role in the transmission of pulse-shaped signals. By definition, it is the time that elapses between the 10% value and the 90% value of a level change, referenced to the lowest and highest levels of the pulse, i.e., the pulse bottom and the pulse top.
The rise time is affected when a pulse passes through a low-pass filter. This degradation is related to the time constant of the low pass. Approximately, the quotient 350/ bandwidth of the lowpass can be applied, with the bandwidth in MHz and the rise time in nanoseconds (ns).
For example, if a lowpass filter has a cutoff frequency of 100 MHz, then a pulse with an extremely short rise time will have a rise time of about 3.5 ns after passing through the lowpass filter. This consideration plays a significant role in the display of pulse edges with oscilloscopes. With digital oscilloscopes, the rise time is calculated from the minimum sampling interval multiplied by 1.6. At a sampling frequency of 500 MHz, for example, corresponding to 2 ns sampling interval, this results in a memory bandwidth of 3.2 ns.