received signal strength (UMTS, GSM) (RSS)
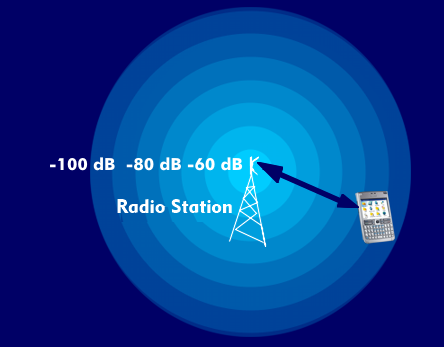
The Received Signal Strength (RSS) is the received field strength. It is the field strength that arrives at the receiver during radio transmission. There is also a high- frequency locating method based on the measurement of the received field strength.
Determination of the received field strength
The received field strength (RSS) depends on the transmitting power and the antenna gain and is attenuated during transmission by the free space attenuation. The latter increases logarithmically with frequency and distance. The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength and the higher the free space attenuation. The received field strength is also influenced by the topology of the terrain between the transmitter and receiver, by buildings and by the humidity of the air.
In isotropic radiation, the field strength of electromagnetic waves decreases with the square of the distance from the transmitter. Therefore, RSS values can be used to draw conclusions about the distance between the receiver and the transmitter, which is what RF-based locating methods take advantage of.
For a radio system to be functional at all, the resulting received field strength must be higher than the sensitivity of the receiver.
HF-based localization
As mentioned earlier, RF-based tracking methods use the received field strength of mobile stations to determine the distance between the transmitter and receiver. However, this assumes that the radiated transmit power is known.
In the case of isotropic radiation of the radio frequency, all points arranged in a circle at a certain distance from the transmitter have the same field strength. This alone does not allow positioning, which can only be realized by RSSI measurement of the received field strength of two or more base stations. With two base stations, the location is still ambiguous. Only when three mobile stations can be included in the measurement can the location of the mobile station be determined unambiguously. The field strength measurement method is used in Cell-ID and Cell of Origin( COO). In the latter case, also in combination with the sectoring of the radio cells by means of Cell Sector( CS).