queued packet and synchronous exchange (DQDB) (QPSX)
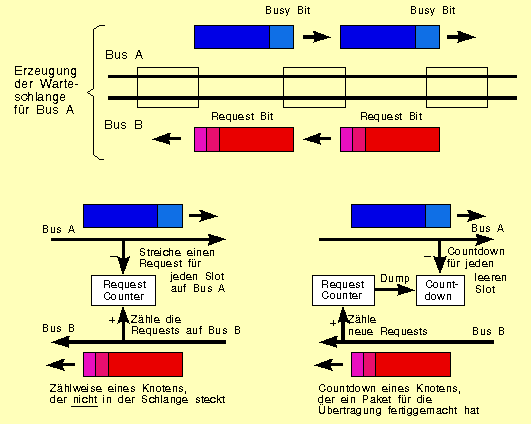
To ensure that the available transmission bandwidth can be used equally by all connected stations in city networks operating with Distributed Queue Dual Bus( DQDB), DQDB networks have implemented a special access method: Queued Packet and Synchronous Exchange (QPSX). QPSX uses a distributed queuing algorithm as a slotted ring. It uses two dual buses running in opposite directions, connected only by the stations.
In this method, all network stations receive information about the overall situation on the network. Stations with a transmit request must inform all stations ahead of them on the transmit bus (A). This is done by means of a request bit via the second bus (B). Since other stations also send requests, the station waits until all requests have been processed. For this purpose, each station has counters that count the requests that have already been sent before and the requests that were sent after its own request.
When it is the station's turn, the data is inserted into the cell. Cells can be unlocked after a station has taken the data.
The 53 byte long data frame of the DQDB cell contains 48 bytes for the data and 5 bytes for the header.