power semiconductor
Power semiconductors are semiconductor devices specifically designed for switching high currents and voltages. While conventional semiconductors switch currents of less than 1 A and voltages of up to 100 V, these arbitrarily selected values are the lower limits for power semiconductors.
At the upper end, the currently feasible technical limits for power switches are at switching voltages of 10 kV and more and at switching currents of several kilo-amperes. For this reason, power semiconductors are used exclusively in power engineering, drive technology and high- voltage engineering.
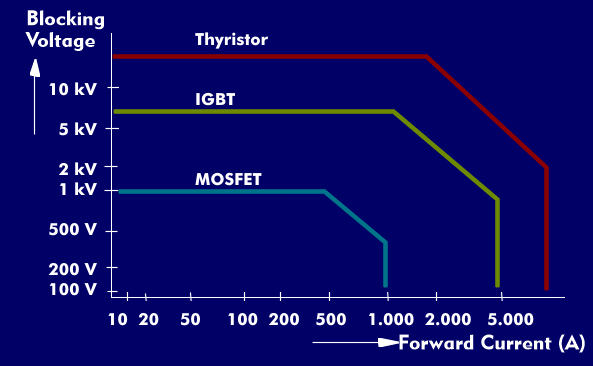
Power semiconductors have developed in parallel with conventional semiconductors since the 1950s and are primarily formed by multilayer semiconductors. The evolution has led from the bipolar transistor to the MOSFET and the thyristor to the high-power Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor( IGBT), the GTO thyristor and the Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor( IGCT).
These power semiconductors differ in their switching voltages and currents, and in their switching powers and frequencies. The former can far exceed 10 mega-volt amperes( MVA) in the case of thyristors, while IGBTs can also easily reach up to 5 MVA and MOSFETs around 20 kVA. The higher the switching power, the lower the switching frequency. While this is less than 1 kHz for thyristors, it rises to about 100 kHz for IGBTs and to well over 100 MHz for MOSFETs.
For power semiconductors, there is a special package with good heat dissipation in the form of the TO leadless package.