plesiochronous digital hierarchy (WAN) (PDH)
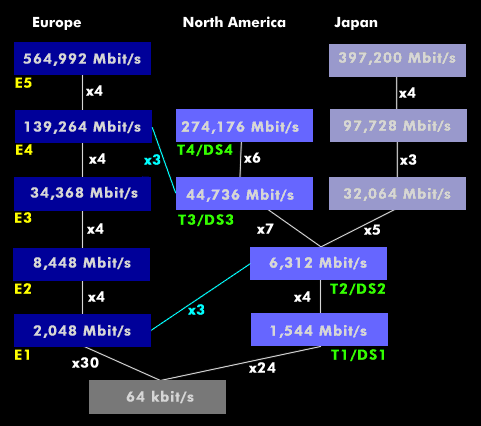
The plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) describes a digital transmission technique for transmission between network nodes that do not have an identical clock. The PDH hierarchy was standardized by the former CCITT in 1972 and has different bit rates. The transmission rates are defined in the ITU-T standards, G Recommendations as G.702; the physical and electrical characteristics of the transmission interfaces under G.703.
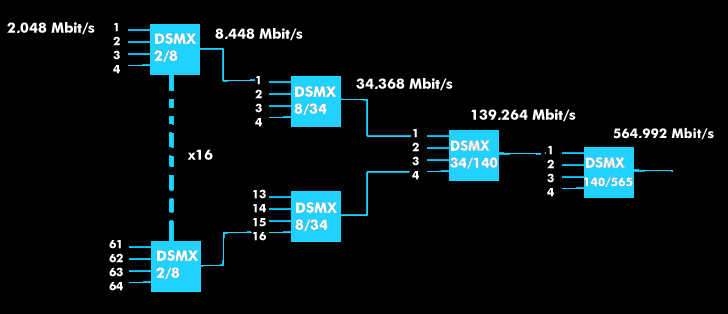
For the basic bit rates with E1 of 2.048 Mbit/s and T1 of 1.544 Mbit/s used in North America and Japan, G.702 provides for a time-division multiplex structure based on 64-kbit/s channels. In the first multiplex stage of E1, 32 channels are combined in accordance with PCM technology, the data rate of E2 is 8.448 Mbit/s and that of E3 is 34.368 Mbit/s. Since 1985, there are also E4 with 139.264 Mbit/s and E5 with 564.992 Mbit/s.
The PDH method has various disadvantages when multiplexing or demultiplexing. PDH is no longer used in new installations and is being continuously replaced by Synchronous Digital Hierarchy( SDH).
The transmission of ATM cells via PDH networks is specified for the E transmission interfaces E1, E3 and E4 and for the DS transmission interfaces DS-1 and DS-3.