phase shift keying (Modulation) (PSK)
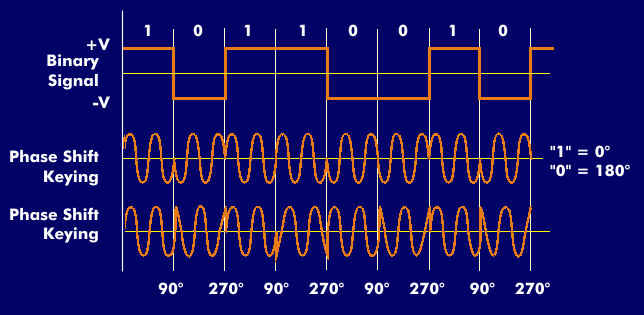
Phaseshift keying (PSK) is a phase modulation for digital signals. With this method, the signal has a constant frequency and a constant amplitude. The phase position of the carrier signal changes abruptly with the rhythm of the digital modulation signal.
In two-cycle phase shift keying (2PSK), the digital "0" is assigned one phase angle, for example 0 degrees, and the digital "1" is assigned the second phase angle of 180 degrees. Phase shift keying with two changes of state is called two-phase shift keying(BPSK). Since the transmission speed is relatively low when shift keying between two states, but at the same time a certain bandwidth is used, methods have been developed in which multiple phase angles are used for shift keying, for example quadrature phase shift keying( QPSK), which stands for 4PSK.
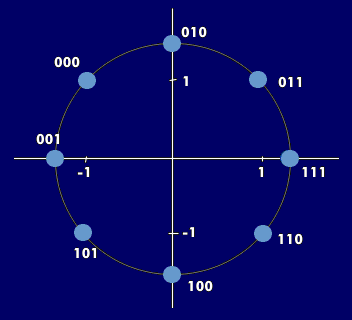
In addition, phase shift keying is combined with amplitude shift keying to achieve a further increase in transmission speed with the same bandwidth. This method is called Quadrature Amplitude Modulation( QAM). Instead of individual bits, the bits are combined into groups of dibits, tribits or quadbits (4PSK, 8PSK, 16PSK) and the carrier frequency is scanned at a specific phase angle with a specific amplitude. Therefore, all symbols lie on a circle and have equal amplitudes.
The QAM method, which achieves the highest transmission rates, is used for transmission in modems, among other things.