phase noise
Phase noise is an irregular, non-periodic change in phase position. This important parameter affects the frequency and modulation behavior of oscillators, mixers and RF generators, and thus communication and radio technologies.
Phase noise arises from the instability of oscillators and manifests itself in minimal frequency deviations. These instabilities are triggered by a wide variety of influences; these can be the noise of the supply voltage, fluctuations in the feedback, the quality factors of the frequency-determining components, temperature fluctuations, and so on. The lower the phase noise, the better the frequency selection capabilities, modulation errors and selectivity, and the lower the bit error rates.
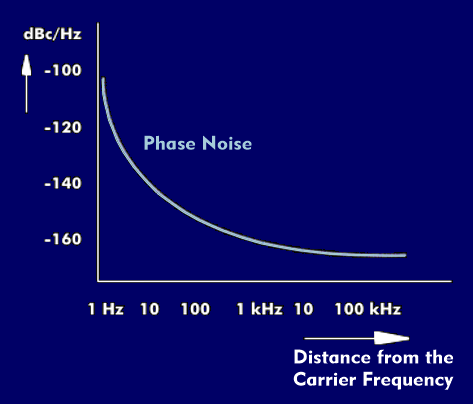
Phase noise is expressed in decibels carrier( dBc) for a given distance from the carrier frequency and is related to a given bandwidth: so, for example, -130 dBc/ Hz at a distance of 10 hertz from the carrier frequency and decreases with distance from the carrier frequency. At 10 kHz carrier spacing, the value could have dropped to -170 dBc.