personal computer (PC)
Personalcomputers(PCs) are the most widely used computers. The term is occupied by the classic IBM PC, which was developed in the early 1980s. In addition, the term was associated by the operating system Disc Operating System( DOS) and later by Windows. Over the years, the personal computer has evolved from a simple computer for word processing to an extremely powerful computer used in both commercial and personal settings.
The structure of personal computers
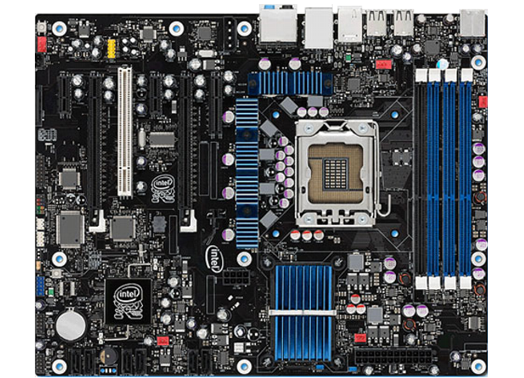
The structure of a personal computer is modular and basically consists of the motherboard with the central processing unit( CPU), RAM, bus systems, interfaces, graphics card, communication components and connectors. The size of the motherboard and the arrangement of the slots and interfaces on the motherboard are largely determined by form factors.
The motherboard and some peripherals are powered by a separate power supply unit. In addition, the basic concept of a PC includes built-in peripherals, such as the hard drive and DVD drives. External peripherals for data input are the keyboard and mouse, and optical output is provided by a monitor.
The components of the motherboard
The central processing unit (CPU) is the central processor whose processing power determines the computer performance. Single-core and multi-core processors are used on CPUs, and ULV ( ultra low voltage) processors are used for better energy efficiency. The various Intel and AMD types are used in their diverse variants of processors. Thus, the Core i5 and Core i7 and AMD's Phenom, Sempron and Athlon. Their clock rates are between 2.5 GHz and 3.5 GHz and their maximum power dissipation, Thermal Design Power( TDP), is between 50 W and 130 W. The different CPUs have Level2 caches of one, two or three megabytes( MB), there are some exceptions with 6 MB and 12 MB.
The main memory, where application data is stored, has storage capacities of up to 16 gigabytes( GB) in powerful devices. However, many operating systems can only manage a memory size of 4 GB. The main memories are designed as memory bars that are plugged into slots on the motherboard. As for the hard disk, PCs have hard disks with storage capacities of a few hundred gigabytes (GB) as standard. There are also hard drives and solid-state drives with several terabytes( TB) of storage capacity.
As for graphics capability through the graphics card, there are on- board or shared-memory graphics cards, the latter using memory space from the main memory. When playing high-definition video, computer games, and displaying 3D graphics, powerful graphics cards with large amounts of memory with Graphics Double Data Rate( GDDR) can be used.
Conceptual differences of personal computers
In terms of concept, PCs work with internal bus systems such as the Extended Industry Standard Architecture( EISA), the PCI bus and its further developments such as the PCI-X bus and the PCI Express( PCIe) to which the individual functional units, such as drive drivers, network cards, communication adapters, etc., have direct access. The performance of PCs is expressed in the bus width, the clock frequency of the central processing unit and the size of the RAM and hard disk. There are various benchmarks for comparing computing power.
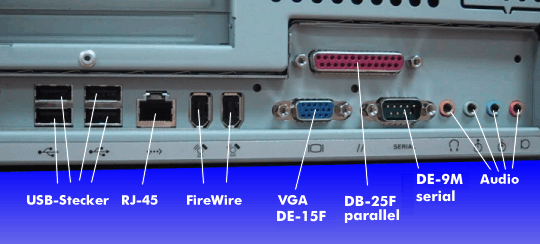
In terms of interfaces, PCs have several USB interfaces, Firewire, PC card slots, slots for memory cards, a VGA interface, connections foraudio and high-performance digital display interfaces like the HDMI interface, the DisplayPort or the GDI interface. For communication, there are wired USB and Ethernet interfaces, wireless connections with WLANs according to 802.11 and Bluetooth.
In terms of design, stationary standard PCs can be desktop, nettop, all-in-one PC or mini-tower and tower models. Mobile computers include laptops, notebooks, subnotebooks, netbooks and tablet PCs. Stationary PCs have Windows as their standard operating system. This operating system, which was introduced by Microsoft as early as 1983, is available in a wide variety of Windows variants that represent different development stages and applications. The standard operating system for Apple devices is Mac OS. Unix and the various Unix variants are also used. All of the operating systems mentioned work with graphical user interfaces.

-Foto-qambo-de_en.png)