optical window
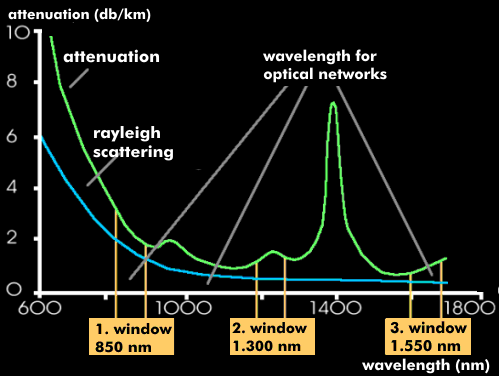
Optical transmission technology with optical fibers uses wavelength ranges that are characterized by low material attenuation. These wavelength ranges are referred to as optical windows.
In optical fibers, scattering and absorption result in wavelength ranges in which attenuation is lower than in other ranges. These ranges are called optical windows and are used for transmission for the different modes. The optical windows are at 850 nm, 1,300 nm and 1,550 nm.
The International Telecommunication Union( ITU) has defined a total of six wavelength ranges in the 2nd and 3rd optical windows (F2, F3) for transmission in optical networks. According to this, the O-band lies in the 2nd optical window, the E-band, S-band, C-band, L-band and U-band in the 3rd optical window. The lower wavelength range at 850 nm (F1) is used for transmission on multimode fibers in local area networks and is specified by the IEEE for Gigabit Ethernet, among other things.
Typical attenuation values are 3 dB/km for 850 nm wavelength and 0.1 dB/km for 1,300 nm with single mode fibers.