open circuit voltage (OCV)
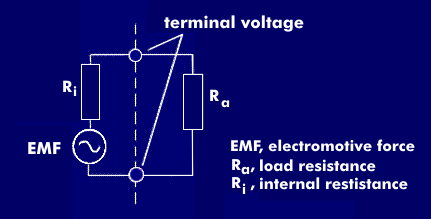
The open circuit voltage is a characteristic value of unloaded voltage sources. As can be seen from the English designation Open Circuit Voltage (OCV), the open circuit voltage is the voltage at the battery terminals when no circuit is connected, i.e. no current flows and therefore no voltage drop can occur at the internal resistance of the voltage source. It is also referred to as the open-circuit voltage.
The open circuit voltage is used for accumulators and batteries, for solar cells, transformers, power supplies and generators and states that it is the terminal voltage measured at the terminals without any circuit or other load being connected.
As long as no current is flowing, the open circuit voltage is equal to the electromotive force( EMF) of the voltage source. The equivalent circuit diagram shows the internal resistance in series with the emf and makes it clear that the open-circuit or source voltage must be unloaded and no current may flow through the internal resistance of the voltage source so that no voltage drop occurs at it. For NiCd batteries, the open-circuit voltage is 1.299 V.
In the case of rechargeable batteries, there is a hysteresis between the open-circuit voltage during charging and discharging. The voltages deviate from each other because of the time-shifted chemical reactions.