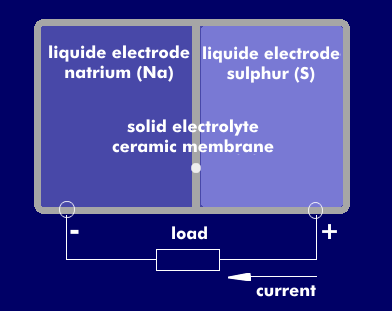
natrium sulphur accumulator (NaS)
The sodium-sulfur (NaS) battery reverses the principle of liquid electrolytes and solid electrodes. Unlike other rechargeable batteries, NaS batteries have a solid electrolyte.
The electrolyte of the NaS battery is a ceramic membrane made of aluminum oxide that separates the reaction chambers. At higher temperatures between 290 and 350 degrees Celsius, the ceramic membrane becomes permeable to ions. The anode is a molten electrode of sodium and the cathode is liquid sulfur.
Sodium-sulfur batteries have an energy density of over 200 Wh/kg and a power density of 100 W/kg. Their efficiency is about 80 %. A disadvantage is the high operating temperature. This is between 290 degrees Celsius and 350 degrees Celsius and ensures that the electrodes remain liquid. In the future, sodium-sulfur batteries will be used as energy storage devices and in electromobility.