mobile WiMAX
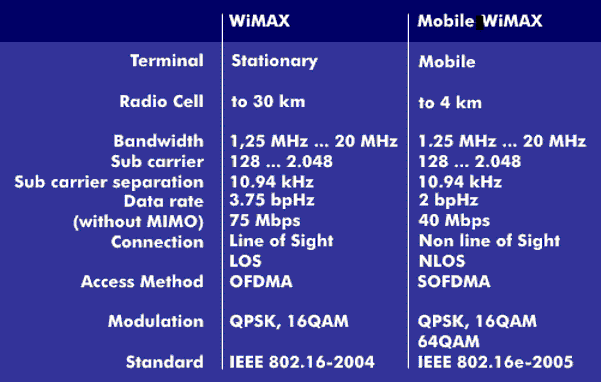
WiMAX knows two deployment variants: the stationary and the mobile, the Mobile-WiMAX. The main difference between the two scenarios is the line of sight( LOS) between the base station( BS) and the mobile station( MS), which characterizes the stationary WiMAX, and the line of sight, Non Line of Sight ( NLOS), which is not required for the mobile WiMAX.
This difference has a direct impact on the data rate, which is lower for mobile WiMAX than for stationary. The transmission specification for the data rate is 2 bits/ Hz, which is almost half of WiMAX. With these specifications, data rates of 40 Mbit/s are achieved over a 20 MHz channel. With the MIMO method, data rates of over 90 Mbit/s are achieved on a 10 MHz channel. Of this, 63 Mbit/s is used for the downlink and 28 Mbit/s for the uplink. With a diameter of 1 km to approx. 4 km, the radio cells are also considerably smaller than those of stationary WiMAX.
Mobile-WiMAX, which is based on the 802.16e-2005 standard, uses Scalable Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access( SOFDMA) with 2,048 subcarriers for transmission. IEEE 802.16e prescribes quadrature phase shift keying (QPKS) or the quadrature amplitude modulations 16QAM and 64QAM as modulationmethods. The latter is only optional. In addition, Mobile-WiMAX uses Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request( HARQ) for efficiency enhancement and different multiplexing schemes such as Frequency Division Duplex ( FDD) or Time Division Duplex( TDD). The radio frequencies of Mobile-WiMAX are between 2 GHz and 11 GHz.