metal oxide semiconductor (Chip) (MOS)
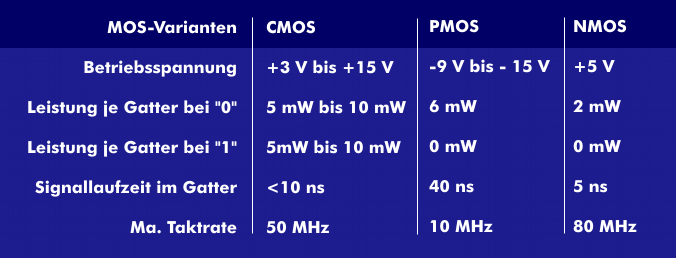
MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technology is a monolithic semiconductor technology for discrete devices and integrated circuits( IC), which is used in the different variants as NMOS (n Channel MOS), PMOS (p Channel MOS), CMOS (Complementary Symmetry Metal Oxide Semiconductor) and MOSFET. The combination of NMOS with a negative charge excess and PMOS with a positive charge excess results in the complementary technology CMOS.
The basis of all MOS technologies is a semiconductor material on which various insulating layers of metal oxides and silicon oxide are vapor-deposited. Since MOS circuits have a very high impedance due to the metal oxide layers, only very low currents are required for control and they also generate hardly any heat loss. However, they are extremely sensitive to static charges, which can lead to the destruction of the component. Therefore, certain safety measures must be observed when working with MOS circuits.
MOS technology is characterized by high integration density and low power consumption and is used in integrated circuits and microprocessors, mostly as CMOS technology.