memory cell
A memory cell is a storage element for two bits, i.e. it can store two states. In this context, one also speaks of a 1-bit memory cell, or bit cell. However, there are also memory cells for 1 byte that consist of eight memory elements.
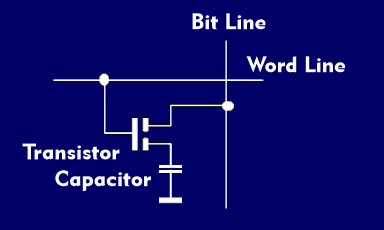
Depending on the memory technology, the memory cell is also designed differently. For example, the memory cell of a Dynamic Random Access Memory( DRAM) or Ferro- RAM( FRAM) consists of a transistor, usually a field-effect transistor( FET), which works as a switching transistor, and a MOS capacitor in which the charge is stored. Such memory cells are called 1T1C memory cells. However, there are also memory cells that consist of two transistors and two MOS capacitors; these are called 2T2C memory cells. The transistor of a memory cell is controlled by two lines: the bit line and the word line. In the case of charge storage, the transistor is switched via the two control lines and charges the capacitor via the read/write amplifiers. The charge information is read out in the reverse direction. The charge state is passed to the I/O logic.
A flash memory uses a MOSFET, which is characterized by its high impedance. Such a MOSFET consists of three silicon electrodes, the gate, the drain and the source. A capacitor is charged via such a high-impedance switch. Unlike bipolar transistors, MOSFETs reach a stable state, which can be conductive or non-conductive. However, since other circuit components are connected to the gate, the gate discharges as soon as power is removed from the circuit. This is prevented in the flash memory cell by incorporating another electrode, the floating gate, into the non-conductive insulating layer between the control gate and the substrate. It has no connection and functions as a charge storage device. Once a charge is applied to the floating gate, it is retained there and prevents the capacitor charge from flowing away. As a result, the flash memory retains its state even after it is turned off.
The floating gate itself is controlled with a quantum mechanical effect in which a higher positive voltage forms a tunnel across which some electrodes from the source gate migrate to the floating gate. A similar technology is charge- trap flash( CTF), which is increasingly used in flash memories As an alternative to floating gate technology, a technology called charge-trap flash (CTF) is increasingly used in NAND flashes, which can achieve higher storage densities.