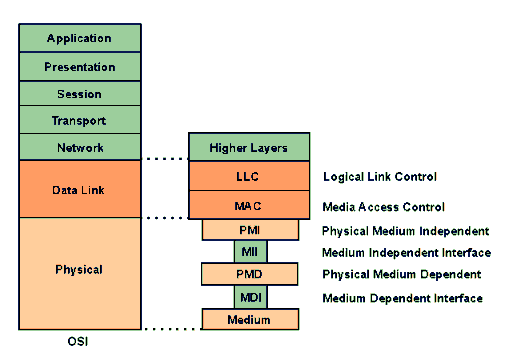
media independent interface (MII)
The Media Independent Interface (MII) was originally the interface between the media access method of Fast Ethernet with the physical transmission medium.
In contrast to the Medium Dependent Interface( MDI) used in normal Ethernet, the MII interface is uniformly pronounced for the different physical media and supports data transmission speeds of10 Mbit/s and 100 Mbit/s and also provides a management interface for monitoring and configuring the lower layers.
The interface's media independence means that components with different physical media - TP cable, fiber, etc. - can be connected to it without the need to redesign the MAC hardware. The MII interface of Fast Ethernet corresponds to the AUI interface in Ethernet. The Medium Independent Interface supports the classic data rate of 10 Mbps as well as that of Fast Ethernet with 100 Mbps. The clock rate is 25 MHz, the number of pins 16. The MII interface can be located inside network components as well as outside. With the R version, Reduced Media Independent Interface( RMII), there is a version with half the number of pins and data lines.
Various variants for Ethernet versions with higher data rates have emerged from the Media Independent Interface. Thus Gigabit Media Independent Interface( GMII), Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RMII), Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface( SGMII), 10 Gigabit Media Independent Interface( XGMII), 10 Gigabit Attachment Unit Interface( XAUI) as well as some Small Form Factor variants.