long term evolution (3GPP) (LTE)
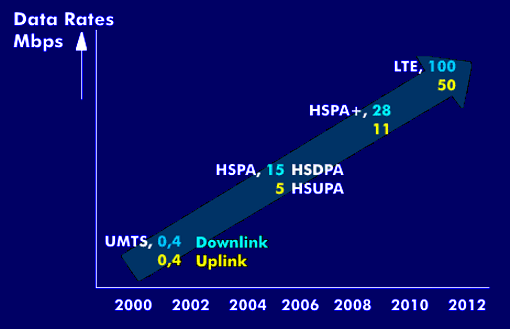
Generations are assigned to the various mobile communications technologies. For example, the GSM standard belongs to the 2nd generation( 2G), UMTS to the 3rd generation( 3G), and High Speed Downlink Packet Access( HSDPA) is assigned to the 3.5th generation. Long Term Evolution( LTE+ is to be regarded as the successor technology to UMTS and HSDPA. It therefore has the chronological classification as 4th generation( 4G).
All high-speed technologies compete for the mobile broadband and mobile Internet market. Long Term Evolution is prioritized by the major operators of the UMTS networks, who have committed themselves to LTE technology worldwide. LTE technology is thus the world's first ever uniform mobile communications standard.
The standardization of LTE
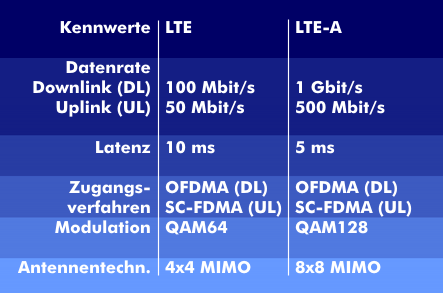
The standardization of LTE technology is defined in 3GPP as Release 8. This technology, in conjunction with Multiple Input Multiple Output( MIMO) and Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access( OFDMA), can transmit peak data rates of 150 Mbit/s in the downlink.
In addition to the higher data rate, LTE technology makes more efficient use of the available frequency range. In the uplink, data rates of 50 Mbit/s are achieved from the mobile device to the base station. The high data rates are achieved by allocating different bandwidths and using the modulation techniques quadrature amplitude modulation( QAM 64) and quadrature phase shift keying( QPSK). Thus, bandwidths of 1.25 MHz, 1.6 MHz, 2.5 MHz, 3 MHz, 5 MHz, 10 MHz, 15 MHz and 20 MHz can be flexibly assigned.
Furthermore, the MIMO technology used in LTE increases the antenna gain and enhances the reception sensitivity because this technology combines multiple antennas to form antenna arrays. Each doubling of the number of antennas causes a 3 dB higher reception level when the antenna signals are linked together and wave superposition occurs. Thus, a 4x4 antenna array has a 3 dB higher receive power than a 2x2 antenna array. In addition, the MIMO LTE concept offers improved suppression of interference and better connection quality.
The technical concept of LTE networks
LTE networks are conceptually similar to other mobile networks. Their central network architecture, the System Architecture Evolution( SAE), is an all- IP architecture with control plane and user plane. The central components of the SAE architecture are formed by the Evolved Packet Core( EPC). The components of the EPC core structure include the Home Subscriber Server( HSS), which stores subscriber data; the Mobility Management Entity( MME), which manages access to the LTE network; the radio base station, referred to as eNodeB in LTE networks; the Serving Gateway( SGW) and the PDN Gateway( PGW); and the mobile device, the User Equipment ( UE).
Transmission frequencies of Long Term Evolution
Several frequency ranges are available for LTE mobile communications in Germany: one frequency range is in the UHF range between 790 MHz and 862 MHz. It is referred to as LTE 800 and is mainly used for LTE in the access area and because of its good propagation characteristics in rural areas. LTE 800 base stations can cover a radius of 10 km. The 800 MHz range is the frequency range freed up by the digital dividend during the switchover to digital TV. This frequency range is subdivided and lies between 791 MHz and 821 MHz and between 832 MHz and 862 MHz. It is used by the mobile communications companies O2 Telefonica, Vodafone and Telekom.
Another frequency range is at 1.8 GHz and was previously used by the German armed forces, and a third is between 2.5 GHz and 2.69 GHz. In this frequency range, various frequency bands are allocated to the network operators Telekom, Vodafone, E-Plus and O2. Long Term Evolution (LTE) operates at the physical level in the downlink with OFDM as the access method; this technology is also known as High Speed OFDM Packet Access( HSOPA). The Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access ( SC-FDMA) access method is used in the uplink.
Long Term Evolution is designed to be an upgrade of existing mobile communications technologies, such as CDMA2000 and Evolution Data Optimized( EVDO). Long Term Evolution Advanced (LTE-A) has already been developed by 3GPP as a successor technology to LTE. Deutsche Telekom has developed a technical intermediate step with LTE+, which has increased the data rate from 100 Mbit/s to 150 Mbit/s.
LTE in the access area
LTE in the access area offers significant speed advantages and low latency. The advantage of this technology is that in the medium term it will be possible to provide broadband service to regional areas that were previously underserved in terms of high-speed Internet access, both stationary and mobile. And for this LTE connection technology, there is a special frequency range that was previously used for terrestrial TV transmission and has been freed up by the digital dividend. It is the UHF range between 790 MHz and 862 MHz. This frequency range is particularly interesting for the wireless connection ofsmartphones to the mobile Internet. In this frequency range, there is a frequency gap between the uplink frequencies and those for the downlink between 823 MHz and 832 MHz. This frequency gap is called the center gap and has been cleared for wireless systems and radio microphones. The advantage of the 800 MHz frequency range is that these UHF frequencies can be used to cover relatively large areas with few radio base stations.
The technical expansion is relatively simple because it can be built on the existing mobile communications infrastructure. Such an LTE network for the connection area consists of the radio base station and an LTE router installed in the house via which the connection to the stationary connection in the house or mobile directly to the smartphone, tablet or notebook are established.

-in-Deutschland_en.png)