leaf spine
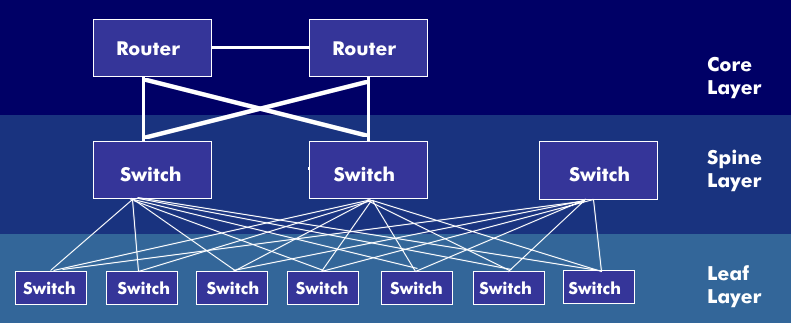
The Leaf Spine architecture is a modern data center architecture that eliminates bottlenecks of the classic data center architecture. The Leaf-Spine model consists of two or three layers: the Core layer, Spine layer, and Leaf layer. The core layer forms the top of the leaf-spine architecture, and the leaf layer forms the bottom layer.
The leaf layer forms the access layer to which the servers and storage units are connected. The Leaf switches are fully meshed and connected to the Spine switches. The meshing ensures that there is no more than one hop between the access switches. This minimizes latency and the likelihood of bottlenecks occurring between access switches. The leaf switches form the access layer that provides network connection points for servers. Each time a connection is made to another server, the same number of switches is traversed.
Data flow between Layer 3 and Layer 2 switches can be routed or switched. To avoid bottlenecks, Leaf-Spine uses Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links( TRILL) or Shortest Path Bridging( SPB) instead of Spanning Tree Protocols( STP). The SPB protocol includes a learning mechanism to determine where hosts and servers are connected to the leaf layer and the shortest loop-free connection to the corresponding MAC addresses.
Above the leaf layer is the spine layer. The spine switches have a high port density and form the core of the architecture model in the two-layer leaf-spine model. In the three-layer architecture, the core is formed by the switches in the core layer. These switches are used to connect to outsourced data centers and the Internet.