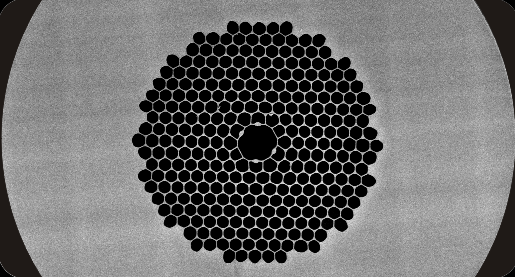
hollow-core fiber
Hollow-core fiber is a microstructure optical fiber(MOF) that differs in structure from conventional optical fib ers. Instead of core glass, the hollow-core fiber uses air for transmission. Its principle is based on the so-called bandgap effect rather than the difference in refractive index between the core glass and cladding glass.
The bandgap effect is expressed in the fact that solids can absorb light because the photon energy is absorbed by excitation of electrons. However, this only affects certain energy bands in which electrons can be excited. When the bandgaps are optimally matched with the energy level of the photons of the light beam, complete light reflection occurs.
In hollow-core fiber, the core glass is replaced by air. The light signal is transported in this air- fiber core. Such a fiber is constructed like a thin tube in which light is transmitted.
The advantage of such a fiber is its attenuation and latency. While in normal glass fibers, due to the refractive index of about 1.5, the speed of light is reduced to about 200,000 km/s, in the hollow core fiber it remains largely unchanged and is 300,000 km/s. In extremely time-critical applications, such as high-speed stock market trading, this can mean a competitive advantage. For example, a time difference of 0.17 ms results for two data centers 100 km apart; calculated from 0.5 ms to 0.33 ms.