heatpipe
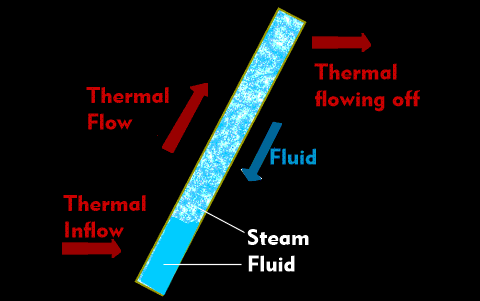
A heat pipe is a tubular heat sink with which heat can be dissipated. In terms of construction, heat pipes are self-contained heat pipes in which there is liquid and negative pressure. Heat dissipation through heat pipes is based on the evaporation of the liquid through constant heat absorption and the subsequent condensation of the vapor and the associated heat release.
At the point where the heat is to be dissipated, the liquid in the heat pipe is heated, it evaporates and rises as vapor to the top, to the cooler area of the heat pipe. There, the vapor cools down, condenses and thus releases the heat and sinks again as a liquid to the hotter area of the heat pipe.
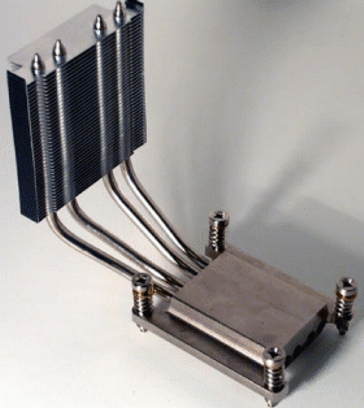
The heat transport is thus much faster than in a metallic heat sink. The heat dissipation of a heat pipe is by a factor of 1,000 to 10,000 times faster than in copper conductors with the same dimensions. The heat pipe is therefore used exclusively to transport heat to the appropriate cooling equipment.
Heatpipes are used in computer technology for coolingcentral processing units( CPU), mainly in laptops and notebooks. Heatpipes are also used for the heat dissipation of LED chips and LED modules, since the high luminous efficacy oflight-emitting diodes increases the heat generation enormously and thus reduces the LED service life.
Since classic heat pipes are relatively large, they cannot be used in mobile devices such as cell phones, palmtops and handhelds. For this area of application, nano heatpipes with a comparable structure but much smaller size and filled with carbon have been developed. Heatpipes with the smallest diameter are already used in embedded component technology in printed circuit boards, where they provide heat dissipation on the board.