hard disk drive (HDD)
Hard disk drives (HDD) are drives with one or more non-replaceable hard disks. The drives are encapsulated so that the hard disks with their sensitive magnetizable surfaces, the hard disk arm and the read/write heads mounted on it are protected against dust and contact. The dust- proof, hermetically sealed hard drive enclosure ensures that neither contaminants nor moisture will affect the operation of the hard drive.
This fully enclosed design was developed by IBM in the 1970s and named the Winchester drive after the Winchester production site in England. The first Winchester drive had a storage capacity of 30 megabytes( MB). Modern hard disks achieve storage capacities of ten terabytes( TB) and above.
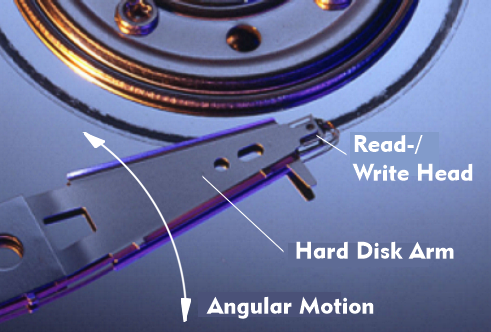
Hard disk arm with read/write heads
If a hard disk drive has several hard disks, then these are arranged concentrically on an axis one above the other and are simultaneously driven by a motor. The movement of the hard disk arm with the read/write heads is also synchronous for all coated surfaces, as all read/write heads are firmly connected to each other via the access arm. A plunger coil system with position control provides control of the access arm and the associated precise positioning of the read/write heads.
The hard disk arm is controlled according to various algorithms, taking into account the angular movement of the hard disk arm. For example, in the First Come First Served( FCFS) algorithm, the rotating arm control is performed in the order in which the jobs are received. In contrast, the Shortest Seek First( SSF) algorithm optimizes the deflection angle of the hard disk arm by always moving to the position closest to the previous one. And with the Elevator algorithm, the existing direction of movement of the hard disk arm is continued until no further sectors need to be addressed in the same direction. Only then is the direction reversed.
When the hard disk drive is switched off, the hard disk arm is placed in a park position.
The rotation and size of hard disks
The rotation speed of hard disks directly affects the access time and data transfer rate. However, it cannot be increased arbitrarily because the remagnetization of the iron oxide particles takes a certain amount of time. Hard disks operate at constant rotational speeds. The standard hard disk with a diameter of 5.25" rotates at rotational speeds of 3,600 rpm, 4,500 rpm, 5,400 rpm, 7,200 rpm, 10,000 rpm and even 15,000 rpm. There are also smaller versions for laptops, notebooks, handhelds, camcorders and MP3 players with 3.5", 2.5", 1.8", 1.0" and 0.85" diameters. These hard drives are referred to as miniature hard drives. An example is the Microdrive from IBM.
The data transfer rates of hard disk drives depend on the data density and the rotation speed. Higher rotation speeds result in higher data transfer rates and shorter access times. In a 3.5" hard drive, the outer track has a length of 28 cm, while the inner track has a length of 11 cm. Since the data density and speed are constant, the data transfer rate decreases the closer the read/write head gets to the inner track. For the outer track this can be 90 MB/s, for the inner track about 40 MB/s.
The interfaces to the personal computer
The connection between the hard disk drive and the computer is made via a hard disk interface, for example via Small Computer System Interface( SCSI), Integrated Drive Electronics( IDE), Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics( EIDE) or Advanced Technology Attachment( ATA). Depending on the SCSI version, transfer rates of between 5 MB/s( SCSI-1) and 40 MB/s, 80 MB/s (Ultra-2 SCSI) and more are theoretically achieved via the SCSI protocol. The same applies to the IDE bus. With the PIO Mode 1 protocol it was still 3.33 MB/s, with Ultra- DMA 2 it is 66.6 MB/s.

-Foto-Western-Digital.png)