hard disk (HD)
Hard disks (HD) are round, non-replaceable discs for storing data. They consist of a thin aluminum disk coated on one or both sides with an extremely thin magnetizable iron oxide layer. Data is stored in this magnetizable surface while the disks rotate at high speed. Hard disks are installed in encapsulated, hermetically sealed hard disk drives.
The principle of hard disk storage
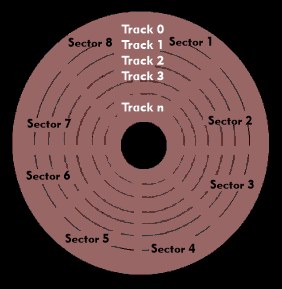
Due to the rotation principle, the magnetic tracks on the hard disks are arranged in concentric circles. Each circle is divided into sectors, which in PC applications comprise 512 data bytes and some address and control bytes. The tracks are longer at the outer edge and decrease in length towards the center of the disk.
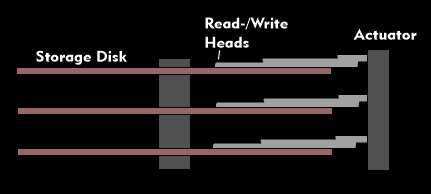
Data is read in and out of the sectors or blocks using read/write heads that float on a cushion of air above the magnetized surface and reach the specified position in fractions of a second via the hard disk arm. To increase storage capacity and reduce access times, several hard disks are arranged one above the other, driven together and synchronously controlled in the scanning mechanism. All sectors of the different disks lie exactly on top of each other, which has led to the term cylinder. Since the various read/write heads are positioned in the same place on the individual hard disks, it is possible to distribute the data over the various disks without any loss of time due to changes in the scanning position.
The different hard disk designs
Hard disks have a standard diameter of 5.25". There are smaller versions for mobile devices, for laptops and notebooks with 3.5", 2.5", 1.8", 1.0" and 0.85" diameters. They rotate at speeds between 3,600 rpm and 15,000 rpm. The storage capacity of modern hard disks currently extends into the single- digit terabyte( TB) range, and the fastest access times are a few milliseconds (ms). A general increase in storage capacity was already achieved years ago with Multiple ZoneBit Recording(ZBR), in which the outer tracks comprise more sectors than the inner ones. This also resulted in a change in sector addressing from the CHS method, Cylinder, Head, Sector (CHS), to the LBA method, Logical Block Addressing (LBA), in which the sectors are numbered consecutively from the outside to the inside. Perpendicular Magnetic Recording( PMR) and Shingled Magnetic Recording( SMR) brought another rapid increase in storage capacity. In PMR technology, the magnetic material is also magnetized in the material depth.
In the early years around 1958, hard disks had storage densities of about 2 kbit/sqinch. Today's hard disks, on the other hand, have storage densities of about 500 Gbit/sqinch, with an increase to about 4 Tbit/sqinch in the offing. At current storage densities, 20,000 tracks or more can be arranged per inch.
The classic hard disk is increasingly being replaced by solid-state drives (SDD), which have much shorter access times.