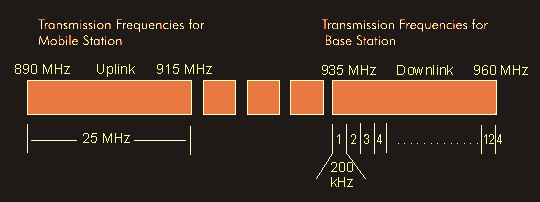global system for mobile communications (GSM)
With the standardization of a European radiotelephone system in the 900 MHz range, the CEPT (Conférence Européenne des Administration des Postes) pursued the goal of a Europe-wide, compatible mobile communications service. The working group that drove standardization is called the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM). Standardization work under GSM focused on digital data transmission, from which the GSM architecture and GSM network were formed.
GSM technology is one of the 2nd generation( 2G) mobile communications systems and is based on digital transmission in time division multiplex with eight channels per radio carrier signal. The transmission rate is 200 kbit/s
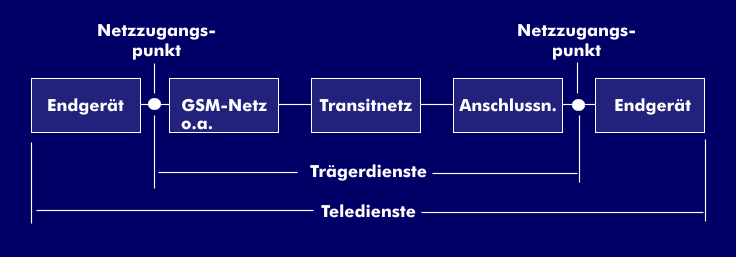
The services in GSM
Various basic and supplementary services are offered in GSM, such as GSM data services, which provide direct access to voice, fax or ISDN data thanks to digital data transmission. In addition, the short message service( SMS) provides point-to-point connections as well as point-to-multipoint connections. Carrier services are pure transport services defined over the lower four layers of the OSI reference model. Data transmission involves synchronous transmissions and asynchronous transmissions with circuit switching and data packet switching.
In addition, GSM offers a number of supplementary and value-added services
ETSI GSM 05.05: names several subsets:
P-GSM: (Primary GSM) uses channels 1 to 124, (890 MHz to 915 MHz uplink, 935 MHz - 960 MHz downlink).
E-GSM: (Extended GSM) uses channels 975 to 1,023 and 1 to 124, (880 MHz to 915 MHz uplink, 925 MHz - 960 MHz downlink).
GSM-R: (Railways GSM) uses channels 955 to 1,023 and 1 to 124, (876 MHz - 915 MHz uplink, 921 MHz - 960 MHz downlink).
GSM 1800: uses channels 512 to 885, (1,710 MHz to 1,785 MHz uplink, 1,805 MHz to 1,880 MHz downlink). GSM 1800 was formerly called Digital Cellular System 1800 MHz( DCS 1800).
GSM 1900: (U.S. Pacific only) uses channels 512 to 810, (1.850 MHz to 1.910 MHz uplink, 1.930 MHz to 1.990 MHz downlink). GSM 1900 is primarily used in the USA and was formerly called PCS 1900(Personal Communications System).